Advanced Search
Content Type: Long Read
The Grand Chamber of the European Court of Human Rights ruled that the UK government’s historical mass interception program violates the rights to privacy and freedom of expression. The Court held that the program “did not contain sufficient “end-to-end” safeguards to provide adequate and effective guarantees against arbitrariness and the risk of abuse.” As a result the Court ruled that UK law "did not meet the “quality of law” requirement and was therefore incapable of keeping the “…
Content Type: Long Read
Summary
This case began in the UK in 2013, following Edward Snowden’s revelations that UK’s GCHQ was secretly intercepting, processing, and storing data concerning millions of people’s private communications, even when those people were of clearly of no intelligence interest (the ‘Tempora’ programme). It was also revealed that the UK government was accessing communications and data collected by the USA’s National Security Agency and other countries’ intelligence agencies. All of this was…
Content Type: Long Read
On 25 May 2021, the European Court of Human Rights issued its judgment in Big Brother Watch & Others v. the UK. Below, we answer some of the main questions relating to the case.
After our initial reaction, below we answer some of the main questions relating to the case.
NOTE: This post reflects our initial reaction to the judgment and may be updated.
What’s the ruling all about?
In a nutshell, one of the world’s most important courts, the Grand Chamber of the European Court of Human…
Content Type: Press release
The Grand Chamber of the European Court of Human Rights has today ruled that UK mass surveillance laws violate the rights to privacy and freedom of expression.
It found that:
The UK’s historical bulk interception regime violated the right to privacy protected by Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights and freedom of expression, protected by Article 10. Particularly it found that:
the absence of independent authorisation,
the failure to include the categories of selectors…
Content Type: Video
This case was made possible because of Edward Snowden’s disclosures in 2013, and through the combined work of Big Brother Watch, American Civil Liberties Union, Amnesty International, Bytes for All, Canadian Civil Liberties Association, Egyptian Initiative for Personal Rights, Hungarian Civil Liberties Union, Irish Council for Civil Liberties, Legal Resources Centre and Liberty.
Content Type: Video
<br />
It’s been a long road, starting at the UK’s Investigatory Powers Tribunal in 2013, but this case would have happened without Ed’s revelations, which revealed the extent of those surveillance programmes. Which is why (around a year ago now) we sat down with him to talk about this case, mass surveillance and what we can do to fight back.
Find out more about the case here: https://privacyinternational.org/legal-action/10-human-rights-organisations-v-united-kingdom
And…
Content Type: Long Read
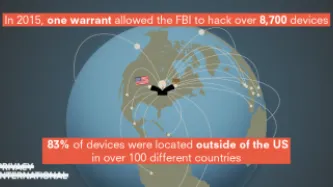
Privacy and security are both essential to protecting individuals, including their autonomy and dignity. Undermining privacy undermines the security of individuals, their devices and the broader infrastructure. People need privacy to freely secure themselves, their information, and fully enjoy other rights. However, a growing number of governments around the world are embracing hacking to facilitate their surveillance activities.
As a form of government surveillance, hacking presents…
Content Type: Long Read
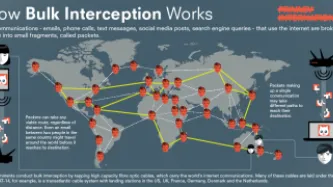
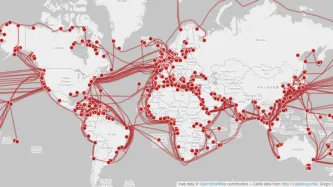
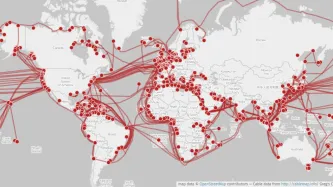
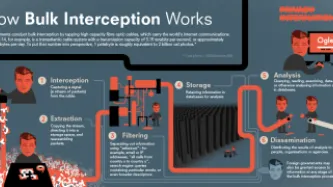
Six years after NSA contractor Edward Snowden leaked documents providing details about how states' mass surveillance programmes function, two states – the UK and South Africa – publicly admit using bulk interception capabilities.
Both governments have been conducting bulk interception of internet traffic by tapping undersea fibre optic cables landing in the UK and South Africa respectively in secret for years.
Both admissions came during and as a result of legal proceedings brought by…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Today, Privacy International, along with nine other NGOs including Liberty and Amnesty International, attended a hearing before the Grand Chamber of the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) to revisit the Court's first ruling on our case challenging UK mass surveillance and intelligence sharing. In September 2018, the First Section of the ECtHR ruled that the UK government's mass interception program violates the rights to privacy and freedom of expression. Notwithstanding the positve aspects…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Federal law enforcement is deploying powerful computer hacking tools to conduct domestic criminal and immigration investigations.
By Alex Betschen, Student Attorney, Civil Liberties & Transparency Clinic, University at Buffalo School of Law
Hacking by the government raises grave privacy concerns, creating surveillance possibilities that were previously the stuff of science fiction. It also poses a security risk, because hacking takes advantage of unpatched vulnerabilities in our…
Content Type: Press release
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
December 21, 2018
CONTACTS:
Alex Betschen, Civil Liberties & Transparency Clinic, alexbets@buffalo.edu, 716–531–6649
Colton Kells, Civil Liberties & Transparency Clinic, coltonke@buffalo.edu, 585–766–5119
Abdullah Hasan, ACLU, ahasan@aclu.org, 646–905–8879
NEW YORK — Privacy International, the American Civil Liberties Union, and the Civil Liberties & Transparency Clinic of the University at Buffalo School of Law filed a lawsuit today…
Content Type: Long Read
This piece was originally published in Just Security.
Earlier this month, the European Court of Human Rights issued a major judgment in three consolidated cases challenging the U.K. government’s mass interception program, which was first revealed by Edward Snowden in 2013. That judgment finds notable deficiencies in the legal framework governing mass interception, rendering the program unlawful under Articles 8 and 10 of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR), which protect the rights…
Content Type: Long Read
Written jointly by Privacy International and the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU).
In a landmark decision earlier this month, the European Court of Human Rights ruled that one of the mass surveillance programs revealed by Edward Snowden violates the rights to privacy and freedom of expression. While the case challenges the U.K. government’s mass interception of internet traffic transiting its borders, the court’s judgment has broader implications for mass spying programs in Europe and…
Content Type: News & Analysis
This piece was originally published on Just Security.
Ten years ago, an FBI official impersonated an Associated Press reporter to lure and track a teenager suspected of sending in prank bomb threats to his school. To find him, the FBI agent, posing as a reporter, sent the teenager links to a supposed story he was working on, but the links were infested with malware that once clicked on quickly exposed the teen’s location. More recently, the FBI has seized and modified websites so…
Content Type: Long Read
Yesterday, the European Court of Human Rights issued its judgement in Big Brother Watch & Others V. the UK. Below, we answer some of the main questions relating to the case.
What's the ruling all about?
In a nutshell, one of the world's most important courts, the European Court of Human Rights, yesterday found that certain UK laws about how intelligence agencies can spy on our internet communications breach our human rights. These surveillance laws have meant that the UK intelligence…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Today was a big day for the privacy of millions of people. The European Court of Human Rights has today ruled that UK laws enabling mass interception of our communications violate the rights to privacy and freedom of expression. This finding is an important victory for human rights and the rule of law.
The judges found that:
The UK’s historical bulk interception regime violated the right to privacy protected by Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) and to free…
Content Type: Long Read
The European Court of Human Rights ruled today that the UK government's mass interception program violates the rights to privacy and freedom of expression. The Court held that the program "is incapable of keeping the 'interference' to what is 'necessary in a democratic society'". This finding is an important victory for human rights and the rule of law. Below, we break down the key parts of the decision.
The Court's ruling comes after a five-year battle against two UK mass surveillance…