Search
Content type: Examples
A woman was killed by a spear to the chest at her home in Hallandale Beache, Florida, north of Miami, in July. Witness "Alexa" has been called yet another time to give evidence and solve the mystery. The police is hoping that the smart assistance Amazon Echo, known as Alexa, was accidentally activated and recorded key moments of the murder. “It is believed that evidence of crimes, audio recordings capturing the attack on victim Silvia Crespo that occurred in the main bedroom … may be found on…
Content type: Examples
Denmark released 32 prisoners as part of an ongoing review of 10,700 criminal cases, after serious questions arose regarding the reliability of geolocation data obtained from mobile phone operators. Among the various problems with the software used to convert the phone data into usable evidence, it was found that the system connected the phones to several towers at once, sometimes hundreds of kilometres apart, recorded the origins of text messages incorrectly and got the location of specific…
Content type: Examples
The Lumi by Pampers nappies will track a child's urine (not bowel movements) and comes with an app that helps you "Track just about everything". The activity sensor that is placed on the nappy also tracks a baby's sleep.
Concerns over security and privacy have been raised, given baby monitors can be susceptible to hackers and any app that holds personal information could potentially expose that information.
Experts say the concept could be helpful to some parents but that there…
Content type: Long Read
By Valentina Pavel, PI Mozilla-Ford Fellow, 2018-2019
Our digital environment is changing, fast. Nobody knows exactly what it’ll look like in five to ten years’ time, but we know that how we produce and share our data will change where we end up. We have to decide how to protect, enhance, and preserve our rights in a world where technology is everywhere and data is generated by every action. Key battles will be fought over who can access our data and how they may use it. It’s time to take…
Content type: Examples
A 19-year-old medical student was raped and drowned in the River Dresiam in October 2016. The police identified the accused by a hair found at the scene of the crime. The data recorded by the health app on his phone helped identify his location and recorded his activities throughout the day. A portion of his activity was recorded as “climbing stairs”, which authorities were able to correlate with the time he would have dragged his victim down the river embankment, and then climbed…
Content type: Examples
The body of a 57-year-old was found in the laundry room of her home in Valley View, Adelaide, in September 2016. Her daughter-in-law who was in the house at the time of the murder claimed that she was tied up by a group of men who entered the house and managed to escape when they left. However, the data from the victim's smartwatch did not corroborate her story.The prosecution alleged that the watch had recorded data consistent with a person going into shock and losing consciousness. "The…
Content type: Examples
The 90-year old suspect when to his stepdaughter's house at San Jose, California for a brief visit. Five days later, his stepdaugter's body, Karen was discovered by a co-worker in her house with fatal lacerations on her head and neck. The police used the data recorded by the victim's Fitbit fitness tracker to determine the time of the murder. It was been reported that the Fitbit data showed that her heart rate had spiked significantly around 3:20 p.m. on September 8, when her stepfather was…
Content type: Examples
On 14 May 2018, the husband of the victim, a pharmacist living in Linthorpe in Middlesbrough, subdued his wife with insulin injection before straggling her. He then ransacked the house to make it appear as a burglary. The data recorded by the health app on the murder’s phone, showed him racing around the house as he staged the burglary, running up and down the stairs. The victim’s app showed that she remained still after her death apart from a movement of 14 paces when her husband moved her…
Content type: Examples
A man from Middletown, Ohio, was indicted in January 2017 for aggravated arson and insurance fraud for allegedly setting fire to his home in September 2016. Ohio authorities decided and succeeded to obtain a search warrant for the data recorded on the pacemaker after identifying inconsistencies in the suspect’s account of facts. Ohio authorities alleged that the data showed that the accused was awake when he claimed to be sleeping. It has been reported that a cardiologist, examining data from…
Content type: Examples
In yet another murder case, a New Hampshire judge ordered Amazon to turn over two days of Amazon Echo recordings in a double murder case in November 2018.
Prosecutors believe that recordings from an Amazon Echo in the Farmington home where two women were murdered in January 2017 may yield further clues as to who their killer might be. Though the Echo was seized when police secured the crime scene, the recordings are stored on Amazon servers.
Timothy Verrill, of Dover, New Hampshire, was…
Content type: News & Analysis
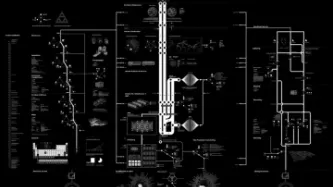
Image: Anatomy of an AI system: a map of the many processes — extracting material resources, data, and human labor — that make an Amazon Echo work. Credit: Kate Crawford and Vladan Joler
With over 6.3 million Amazon Echo devices worldwide, there is a good chance these constantly active devices will record criminal behavior.
Bloomberg, who recently reported on yet another creepy feature, that Amazon workers are listening to what you tell Alexa, were told by workers…
Content type: Long Read
For International Women’s Day 2019, Privacy International looks at some of the key themes around the intersection of gender rights and the right to privacy and we review the work we and our partners have done on those topics.
When dealing with cases of non-consensual sharing of intimate images, often known as ‘revenge porn,’ or doxxing, where a person’s personal details are shared publicly, the link between privacy and online-gender-based violence is very clear. Privacy…
Content type: Report
When you rent a car at the airport, use a car-share for a family day trip, one of the first things you are likely to do before setting off on your journey, is to connect your phone to the car. You switch on the Bluetooth and see a list of other people’s phones that were previously connected - Mike’s iPhone, Samsung Galaxy, Bikerboy_Troi, Dee Dee. You input your journey into the navigation, perhaps noticing stored locations of previous drivers.
Seems fairly innocuous? Wrong. Your name and…
Content type: Examples
For a period between the end of October and November 3 2016 the heating and hot water systems in two buildings in the city of Lappeenranta, Finland were knocked out by a distributed denial of service attack designed to make the systems fail. The systems responded by repeatedly rebooting the main control circuit, which meant that the heating was never working - at a time when temperatures had already dropped below freezing. Specialists in building maintenance noted that companies often skimp on…
Content type: Examples
In 2017, when user Robert Martin posted a frustrated, disparaging review of the remote garage door opening kit Garadget on Amazon, the peeved owner briefly locked him out of the company's server and told him to send the kit back. After complaints on social media and from the company's board members, CEO Denis Grisak reinstated Martin's service. The incident highlighted the capricious and fine-grained control Internet of Things manufacturers can apply and the power they retain over devices…
Content type: Examples
Connecticut police have used the data collected by a murder victim's Fitbit to question her husband's alibi. Richard Dabate, accused of killing his wife in 2015, claimed a masked assailant came into the couple's home and used pressure points to subdue him before shooting his wife, Connie. However, her Fitbit's data acts as a "digital footprint", showing she continued to move around for more than an hour after the shooting took place. A 2015 report from the National Institute of…
Content type: Examples
A 2017 lawsuit filed by Chicagoan Kyle Zak against Bose Corp alleges that the company uses the Bose Connect app associated with its high-end Q35 wireless headphones to spy on its customers, tracking the music, podcasts, and other audio they listen to and then violates their privacy rights by selling the information without permission. The case reflects many of the concerns associated with Internet of Things devices, which frequently arrive with shoddy security or dubious data…
Content type: Case Study
Invisible and insecure infrastructure is facilitating data exploitation
Many technologies, including those that are critical to our day-to-day lives do not protect our privacy or security. One reason for this is that the standards which govern our modern internet infrastructure do not prioritise security which is imperative to protect privacy.
What happened?
An example of this is Wi-Fi, which is now on its sixth major revision (802.11ad). Wi-Fi was always designed to be a verbose in…
Content type: Report
The smart city market is booming. National and local governments all over the world expect their cities to become more efficient, more sustainable, cleaner and safer by integrating technology, increasing data generation and centralising data to provide better services. From large multinationals to small start-ups, companies want their slice of the multi-billion dollars per year pie of municipal budgets and long-term government contracts.
But do smart cities even exist? And are our cities…
Content type: Case Study
Our connected devices carry and communicate vast amounts of personal information, both visible and invisible.
What three things would you grab if your house was on fire? It’s a sure bet your mobile is going to rank pretty high. It’s our identity, saying more about us than we perhaps realise. It contains our photos, calendar, internet browsing, locations of where we go, where we’ve been, our emails, social media. It holds our online banking, notes with half written poems, shopping lists, shows…
Content type: Case Study
As society heads toward an ever more connected world, the ability for individuals to protect and manage the invisible data that companies and third parties hold about them, becomes increasingly difficult. This is further complicated by events like data breaches, hacks, and covert information gathering techniques, which are hard, if not impossible, to consent to. One area where this most pressing is in transportation, and by extension the so-called ‘connected car’.
When discussing connected…
Content type: News & Analysis
For as long as automobiles have been around, manufacturers have been trying to find ways of putting more technology inside of cars, oftentimes sold as value-added services for their customers, whether that be 8-tracks of the 1960s and 1970s, the enhancement to security of central locking of the 1980s and 1990s, or the introduction of satellite navigation in the 2000s.
Today, as our technologies become ‘smarter’, so do the risks to our personal privacy. This especially true as society is on the…