Search
Content type: Long Read
Over the last two decades we have seen an array of digital technologies being deployed in the context of border controls and immigration enforcement, with surveillance practices and data-driven immigration policies routinely leading to discriminatory treatment of people and undermining peoples’ dignity.And yet this is happening with little public scrutiny, often in a regulatory or legal void and without understanding and consideration to the impact on migrant communities at the border and…
Content type: Long Read
Covid Apps are on their way to a phone near you. Is it another case of tech-solutionism or a key tool in our healthcare response to the pandemic? It’s fair to say that nobody quite knows just yet.
We’ve been tracking these apps since the early days. We’ve been monitoring Apple and Google closely, have been involved in the UK’s app process, our partners in Chile and Peru have been tracking their governments’ apps, and more.
Of course privacy concerns arise. But only a simplistic analysis would…
Content type: News & Analysis
Lockdowns and quarantines are an extraordinary measure that help in slowing down the global COVID-19 pandemic, and protecting the population.
However, they come at an even higher cost to some individuals, such as victims of domestic violence, persons in a vulnerable situation, and human rights defenders, who face specific threats that are exacerbated by measures taken by governments to address the global pandemic.
In that context, states should adopt special measures to keep those people…
Content type: Examples
An engineering and computer science professor and his team from The Ohio State University discovered a design flaw in low-powered Bluetooth devices that leaves them susceptible to hacking.
Zhiqiang Lin, associate professor of computer science and engineering at the university, found the commonly used Bluetooth Low Energy devices, such as fitness trackers and smart speakers, are vulnerable when they communicate with their associated apps on the owner’s mobile phone.
"There is a fundamental…
Content type: Examples
The Belgian Minister of Public Health has approved a programme under which telephone companies Proximus and Telenet will transfer some of their their data to the private third-party company Dalberg Data Insights in order to help combat the coronavirus epidemic; Orange has also agreed "in principle". The details are still to be agreed pending a legal and technical analysis of the proposed project. So far it has been reported that location data and real-time tracking would be used to assess the…
Content type: Examples
The Israeli prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, has authorised the country's internal security agency to use a previously secret tranche of mobile phone geolocation data, gathered to combat terrorism, to retrace the movements of individuals with confirmed cases of the coronavirus and identify people they've interacted with who should be quarantined. After Parliament's Secret Services Subcommittee ended its discussions without approving the measure, Netanyahu said the government would approve…
Content type: Examples
A phone-tracking system used by SAPOL for criminal investigations was used to better understand where a coronavirus-infected 60-year-old couple, who had travelled from Wuhan to visit relatives, roamed in Adelaide in order to identify people who might have been exposed, according to the South Australian police commissioner. Police used a program that only requires a phone number to initiate a download of where the phone has been used; to use it they must meet a legislative threshold…
Content type: Examples
Hakob Arshakyan, Armenia's minister of the high technology industry, has convened a research group comprising experts in IT and AI has been convened to collect and analyse data on the spread of coronavirus, compare it with the data collected by international partners, and develop forecasts. The minister believes that the research group's work will help provide accurate and reliable information that will help coordinate and manage containment efforts. As of March 19, Armenia had confirmed 122…
Content type: Examples
The "safety guidance texts" sent by health authorities and district offices in South Korea are causing information overload and have included embarrassing revelations about infected people's private lives. A text may include, for example, a link to trace the movements of people who have recently been diagnosed with the virus. Clicking on the link takes the user to the website of a district office that lists the places the patient had visited before testing positive. In one case, a man in his…
Content type: News & Analysis
In mid-2019, MI5 admitted, during a case brought by Liberty, that personal data was being held in “ungoverned spaces”. Much about these ‘ungoverned spaces’, and how they would effectively be “governed” in the future, remained unclear. At the moment, they are understood to be a ‘technical environment’ where personal data of unknown numbers of individuals was being ‘handled’. The use of ‘technical environment’ suggests something more than simply a compilation of a few datasets or databases.
The…
Content type: Impact Case Study
What HappenedOn 5 June 2013, The Guardian published the first in a series of documents disclosed by Edward Snowden, a whistleblower who had worked with the NSA. The documents revealed wide-ranging mass surveillance programs conducted by the USA’s National Security Agency (NSA) and the UK’s Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), which capture the communications and data of hundreds of millions of people around the world. In addition to revealing the mass surveillance programs of the NSA…
Content type: News & Analysis
Why is a privacy organisation working with the humanitarian sector, and why does it matter? We may seem like strange bedfellows, but today's ever-growing digital world means that, more and more, people who receive humanitarian assistance are being exposed to unexpected threats.
According to the 2018 Global Humanitarian Overview, there are more than 134 million people across the world in need humanitarian assistance. Of these, about 90.1 million will receive aid of some form. It is…
Content type: Long Read
It’s 15:10 pm on April 18, 2018. I’m in the Privacy International office, reading a news story on the use of facial recognition in Thailand. On April 20, at 21:10, I clicked on a CNN Money Exclusive on my phone. At 11:45 on May 11, 2018, I read a story on USA Today about Facebook knowing when teen users are feeling insecure.
How do I know all of this? Because I asked an advertising company called Quantcast for all of the data they have about me.
Most people will have never heard of…
Content type: Examples
In 2013, Edward Snowden, working under contract to the US National Security Agency for the consultancy Booz Allen Hamilton, copied and leaked thousands of classified documents that revealed the inner workings of dozens of previously unknown surveillance programs. One of these was PRISM, launched in 2007, which let NSA use direct access to the systems of numerous giant US technology companies to carry out targeted surveillance of the companies' non-US users and Americans with foreign contacts by…
Content type: News & Analysis
This piece originally appeared here.
We are much more than our physical selves. We are also digital. Every moment we generate more data. Although sometimes this data is under our control, increasingly it is not. This uncontrolled data—this metadata—is often generated as a result of our interactions, movements, sentiments, and even our inaction. Despite being beyond our control, our metadata is still accessible to many. Hardly a day goes by without a news story or global event involving data: a…
Content type: Examples
Because banks often decline to give loans to those whose "thin" credit histories make it hard to assess the associated risk, in 2015 some financial technology startups began looking at the possibility of instead performing such assessments by using metadata collected by mobile phones or logged from internet activity. The algorithm under development by Brown University economist Daniel Björkegren for the credit-scoring company Enterpreneurial Finance Lab was built by examining the phone records…
Content type: Examples
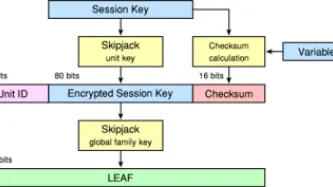
A new examination of documents detailing the US National Security Agency's SKYNET programme shows that SKYNET carries out mass surveillance of Pakistan's mobile phone network and then uses a machine learning algorithm to score each of its 55 million users to rate their likelihood of being a terrorist. The documents were released as part of the Edward Snowden cache. The data scientist Patrick Ball, director of research at the Human Rights Data Analysis Group, which produces scientifically…
Content type: Impact Case Study
PI and our global partners have been at the forefront of challenging communications data retention for over a decade.
What is the problem
Communications data, also known as metadata, tells a story about your digital activity and answers the who, when, what, and how of a specific communication. While communications data doesn't include the contents of a message, all of the other information about the message can be very revealing about people, their habits, thoughts, health and personal…
Content type: Impact Case Study
What happenedThe Clinton Administration kicked off the cypto-wars in 1993 with the Clipper Chip. The continued application of export controls restrained the deployment of strong cryptography in products at a key moment of internet history: as it began to be embedded in software and networking. What we didIn the early phases of the crypto-wars we placed pressure on global industry to implement encryption in their products. We ran campaigns and events across the world on the need for strong…
Content type: Impact Case Study
What is the problem
For over two decades we have been documenting an alarming use and spread of surveillance. It is no longer just the wars on terror or drugs or migration that is driving this trend. The management of health crises and distribution of welfare regularly are among others being used to justify this turn to increasingly invasive forms of surveillance. From country to country we see the same ideas and the same profiteers expanding their reach.
When we first released our report on…
Content type: Impact Case Study
What is the problem
Business models of lots of companies is based on data exploitation. Big Tech companies such Google, Amazon, Facebook; data brokers; online services; apps and many others collect, use and share huge amounts of data about us, frequently without our explicit consent of knowledge. Using implicit attributes of low-cost devices, their ‘free’ services or apps and other sources, they create unmatched tracking and targeting capabilities which are being used against us.
Why it is…
Content type: Impact Case Study
What happenedGovernments continuously seek to expand their communications surveillance powers. In the 1990s it was in the context of applying telephone surveillance laws to the internet. In the 2000s a spate of new laws arrived in response to 9/11. Expansions were then sought to monitor over-the-top services within the framing of Web 2.0. Then in the post-Snowden environment Governments rushed to legislate their previously secret powers.What we didWe supported…