Search
Content type: Examples
Facebook's scientists are analysing location data about compliance with social distancing recommendations in various countries using information from a private vault of location information its apps have collected. The analysis shows that only "very modest" changes in habits in the US, France, and the UK, and much more substantial change in Spain and Italy between mid-February and mid-March. Other companies such as Google and Apple, may also be able to contribute insights into public behaviour…
Content type: Examples
Because tracking and limiting the movement of those suspected to be carrying COVID-19 carriers has been a factor in flattening the exponential curve of cases in places like Singapore, Taiwan, and South Korea, Professor Marylouise McLaws, a technical advisor to the WHO's Infection Prevention and Control Global Unit and a professor at the University of New South Wales, believes that we should use travellers' smartphones to electronically monitor their compliance with self-isolation orders.…
Content type: Examples
According to information collected by Le Temps, telco Swisscom will use SIM card geolocation data to communicate to federal authorities when more than 20 phones are detected in an 100 square meters area. Gathering of more than 5 people are forbidden in Switzerland since March 21.
Data collected by the telco should theoretically only come from public areas and not private building. This data will be anonymised and aggregate before being passed to the health authorities (Office fédéral de la…
Content type: Examples
The Belgian Minister of Public Health has approved a programme under which telephone companies Proximus and Telenet will transfer some of their their data to the private third-party company Dalberg Data Insights in order to help combat the coronavirus epidemic; Orange has also agreed "in principle". The details are still to be agreed pending a legal and technical analysis of the proposed project. So far it has been reported that location data and real-time tracking would be used to assess the…
Content type: Examples
Researchers at the University of Oxford are working with the UK government on an app similar to the smartphone tracking system China developed to alert people who have come in contact with someone infected with the coronavirus. The British app, which would be associated with the country's National Health Service,, would rely on the public volunteering to share their location data out of a sense of civic duty rather than, as in China, compulsion. The service would not publish the movements of…
Content type: Examples
Russia has set up a coronavirus information centre to to monitor social media for misinformation about the coronavirus and spot empty supermarket shelves using a combination of surveillance cameras and AI. The centre also has a database of contacts and places of work for 95% of those under mandatory quarantine after returning from countries where the virus is active. Sherbank, Russia's biggest bank, has agreed to pay for a free app that will provide free telemedicine consultations.
Source:…
Content type: Examples
The Israeli prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, has authorised the country's internal security agency to use a previously secret tranche of mobile phone geolocation data, gathered to combat terrorism, to retrace the movements of individuals with confirmed cases of the coronavirus and identify people they've interacted with who should be quarantined. After Parliament's Secret Services Subcommittee ended its discussions without approving the measure, Netanyahu said the government would approve…
Content type: Examples
The Ecuadorian government has authorised tracking mobile phones via GPS satellite to ensure that citizens do not break mandatory quarantine after six violators were identified.
Source: https://www.ecuadortv.ec/noticias/covid-19/romo-vigilancia-epidemiologico-covid19-?
Writer: Ecuador TV
Publication: Ecuador TV
Content type: Examples
Among the Chinese companies making efforts to help the country respond to the coronavirus are the technology giants Alibaba, Baidu, ByteDance, Tencent, Xiaomi, and Foxconn. In order to fight misinformation, Baidu created a map layer on top of its standard Map App that shows real-time locations of confirmed and suspected cases of the virus so that people can avoid hot spots. Qihoo 360 has launched a platform travellers can use to check if anyone on their recent train or plane trips has since…
Content type: Examples
Technology entrepreneurs within Belgium would like to introduce a health code app similar to China's Alipay Health Code that would control individuals' movements based on their health status. The government has engaged privacy experts from the Belgian data protection authority and Ghent University to consider the possibility, despite the country's strict privacy laws, which have no equivalent in China..
Source: https://www.apache.be/gastbijdragen/2020/03/18/hoe-het-…
Content type: Examples
A phone-tracking system used by SAPOL for criminal investigations was used to better understand where a coronavirus-infected 60-year-old couple, who had travelled from Wuhan to visit relatives, roamed in Adelaide in order to identify people who might have been exposed, according to the South Australian police commissioner. Police used a program that only requires a phone number to initiate a download of where the phone has been used; to use it they must meet a legislative threshold…
Content type: Examples
UK: O2 shares aggregated location data with government to test compliance with distancing guidelines
Mobile network operator O2 is providing aggregated data to the UK government to analyse anonymous smartphone location data in order to show people are following the country's social distancing guidelines, particularly in London, which to date accounts for about 40% of the UK's confirmed cases and 30% of deaths. The project is not designed to monitor individuals. Lessons from the impact on London of travel restrictions could then be applied in the rest of the country. The government says it has…
Content type: Examples
BT, owner of UK mobile operator EE, is in talks with the government about using its phone location and usage data to monitor whether coronavirus limitation measures such as asking the public to stay at home are working. The information EE supplies would be delayed by 12 to 24 hours, and would provide the ability to create movement maps that show patterns. The data could also feed into health services' decisions, and make it possible to send health alerts to the public in specific locations.…
Content type: Examples
Thailand's National Broadcasting and Telecommunication Commission (NBTC) provided a SIM card to every foreigner and Thai who had travelled from countries that have have been designated as "high risk" for COVID-19 infections (at the time, China, Hong Kong, South Korea, Italy, and Macau). According to NBTC secretary-general Thakorn Tanthasit, the AoT Airports' new application had more than 7,000 downloads in its first five days. The sim card will be used together with the AoT Airports application…
Content type: Examples
With 6,300 COVID-19 cases and more than 40 reported deaths, the South Korean government launched a smarphone app (Android first, iPhone due on March 20) to monitor citizens on lockdown as part of its "maximum" action to contain the outbreak. The app keeps patients in touch with care workers and uses GPS to keep track of their location to ensure they don't break quarantine. The government said the tracking was essential to manage the case load (at the time, 30,000 people) and prevent "…
Content type: Examples
The "safety guidance texts" sent by health authorities and district offices in South Korea are causing information overload and have included embarrassing revelations about infected people's private lives. A text may include, for example, a link to trace the movements of people who have recently been diagnosed with the virus. Clicking on the link takes the user to the website of a district office that lists the places the patient had visited before testing positive. In one case, a man in his…
Content type: Examples
Russian authorities are using surveillance cameras, facial recognition systems, and geolocation to enforce a two-week quarantine regime affecting 2,500 people. Chinese citizens are banned from entering Russia; Russians and citizens of other countries who arrive from China are required to go through two weeks of quarantine. Police raid hotels to find Chinese citizens who arrived before border controls began, and bus drivers have been ordered to call their dispatchers if they see Chinese citizens…
Content type: Examples
The German mobile operator Deutsche Telekom announced in a press conference on RKI Live that it had passed on, anonymised, its users' movement data to the Robert-Koch Institute to study the extent to which the population would follow the government's restrictions. RKI president Lothar Wieler said this data is also available for purchase, but was given to RKI at no charge.
Source: https://frask.de/coronavirus-deutscher-mobilfunkbetreiber-gibt-bewegungsdaten-weiter/
Content type: Examples
The Austrian telecom operator A1 has voluntarily provided the government with "anonymized" location data of its customers for the first two Saturdays in March. The data shows that citizens have significantly reduced their social contacts. After critics expressed privacy concerns, the company issued a statement saying that: the movement profiles have been available for some time in a collaborative projects with a spinoff from the Graz University of Technology; no conclusions can be drawn about…
Content type: Examples
Ministers have permitted the Shin Bet security service to "use the cellular phone data of carriers of the disease to retrace their steps and identify anyone they may have infected", and will relay the information to the Health Ministry, which will send a message to those who were within two meters (6.6 feet) of the infected person for 10 minutes or more, telling them to go into quarantine. An update to the original order has extended the period during which it is in force from 30 days until the…
Content type: Examples
Software on smartphones dictates whether an individual should be quarantined. Chinese citizens in 200 cities, beginning with Hangzhou, are required to install the Alipay Health Code app, developed by Hangzhou's local government with the help of Alipay owner Ant Financial, on their smartphones. After users fill in a form with personal details, the software generates a QR code in one of three colors. Green enables its holder to move about unrestricted. Those with yellow codes may be asked to stay…
Content type: Examples
Denmark released 32 prisoners as part of an ongoing review of 10,700 criminal cases, after serious questions arose regarding the reliability of geolocation data obtained from mobile phone operators. Among the various problems with the software used to convert the phone data into usable evidence, it was found that the system connected the phones to several towers at once, sometimes hundreds of kilometres apart, recorded the origins of text messages incorrectly and got the location of specific…
Content type: Long Read
Image credit: Emil Sjöblom [ShareAlike 2.0 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.0)]
Prepaid SIM card use and mandatory SIM card registration laws are especially widespread in countries in Africa: these two factors can allow for a more pervasive system of mass surveillance of people who can access prepaid SIM cards, as well as exclusion from important civic spaces, social networks, and education and health care for people who cannot.
Mandatory SIM card registration laws require that people provide personal…
Content type: Long Read
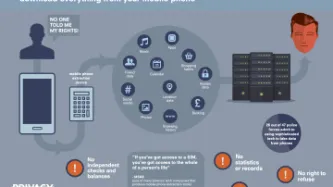
Imagine that every time you want to attend a march, religious event, political meeting, protest, or public rally, you must share deeply personal information with police and intelligence agencies, even when they have no reason to suspect you of wrongdoing.
First, you need to go to the police to register; have your photo taken for a biometric database; share the contacts of your family, friends, and colleagues; disclose your finances, health records, lifestyle choices, relationship status, and…
Content type: Explainer graphic
Content type: Examples
As GPS began being increasingly incorporated into smartphones, satnav manufacturers like the Dutch company TomTom were forced to search for new revenue streams. In 2011, TomTom was forced to apologise when the Dutch newspaper AD reported that the company had sold driving data collected from customers to police, which used it to site speed cameras in locations where speeding was common. TomTom said that any information it shares had been anonymised; however, in response to the newspaper story…
Content type: Examples
A new examination of documents detailing the US National Security Agency's SKYNET programme shows that SKYNET carries out mass surveillance of Pakistan's mobile phone network and then uses a machine learning algorithm to score each of its 55 million users to rate their likelihood of being a terrorist. The documents were released as part of the Edward Snowden cache. The data scientist Patrick Ball, director of research at the Human Rights Data Analysis Group, which produces scientifically…
Content type: Press release
Below is a joint statement from Privacy International and Bytes for All.
This Friday, 27 September, marks the conclusion of the 24th session of the UN Human Rights Council, a session which has, for the first time, seen issues of internet surveillance in the spotlight. Privacy International and Bytes for All welcome the attention given at the Human Rights Council to this issue. However, we are concerned about developments which took place that threaten privacy rights and freedom of…
Content type: Press release
Privacy International today received an email from Saul Olivares, Sales and Marketing Director of Creativity Software, in response to the letter we sent to Creativity CEO Richard Lee yesterday.
Mr Olivares directed PI to an attached statement, in which Creativity stated that it was:
…proud to be a supplier of world class technology to MTN, in Iran and other countries. MTN is a company with the vision of being the leading telecommunications provider in emerging markets, with an avowed mission…
Content type: News & Analysis
Image source
This is a guest post by Zoë Blackler.
If you want to know how the UK came to be the most watched nation in the world, with CCTV on every corner, you need to go back to 1942: the now ubiquitous policing aid was first developed for use in missile testing by the German military.
Tear gas, GPS trackers, pain rays, and surveillance drones - technologies developed by the military for use against foreign enemies have a habit of finding their way into the hands…