Advanced Search
Content Type: Long Read
Privacy and security are both essential to protecting individuals, including their autonomy and dignity. Undermining privacy undermines the security of individuals, their devices and the broader infrastructure. People need privacy to freely secure themselves, their information, and fully enjoy other rights. However, a growing number of governments around the world are embracing hacking to facilitate their surveillance activities.
As a form of government surveillance, hacking presents…
Content Type: Press release
Today, the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) has handed down a decision in a case brought by Privacy International and a coalition of internet and communications service providers and campaign groups including the Chaos Computer Club (Germany), GreenNet (UK), Jinbonet (Korea), May First/People Link (US), and Riseup (US) (the “coalition”).The case challenges the conduct of hacking operations abroad by one of the UK’s intelligence agencies, the Government Communications…
Content Type: News & Analysis
The Watson/Tele2 decision of the CJEU concerned section 1 and 2 of DRIPA and the Data Retention Regulations 2014. This contained the legislative scheme concerning the power of the Secretary of State to require communications service providers to retain communications data. Part 3 of the Counter-Terrorism and Security Act 2015 amended DRIPA so that an additional category of data - that necessary to resolve Internet Protocol addresses - could be included in a requirement to retain…
Content Type: Advocacy
RESPONSE OF PRIVACY INTERNATIONAL TO THE CONSULTATION ON THE GOVERNMENT’S PROPOSED RESPONSE TO THE RULING OF THE COURT OF JUSTICE OF THE EUROPEAN UNION ON 21 DECEMBER 2016 REGARDING THE RETENTION OF COMMUNICATIONS DATA
[Full response below]
Introduction
The consultation is in response to the judgment in Tele2 Sverige AB v Post-och telestyrelsen (Case-203/15) and R (Watson) v Secretary of State for the Home Department (Case C-698/15) [“Watson judgment”].
The case concerned…
Content Type: Explainer
In 2000, the Government told Parliament that the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 (RIPA) was the total extent of surveillance powers that were needed. However, within weeks of RIPA receiving Royal Assent, a report from UK law enforcement was leaked, stating that the power the Government truly wanted was companies to retain communications data on all their users.
Immediately after 9/11 as governments around the world over-reached with new pieces of…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Federal law enforcement is deploying powerful computer hacking tools to conduct domestic criminal and immigration investigations.
By Alex Betschen, Student Attorney, Civil Liberties & Transparency Clinic, University at Buffalo School of Law
Hacking by the government raises grave privacy concerns, creating surveillance possibilities that were previously the stuff of science fiction. It also poses a security risk, because hacking takes advantage of unpatched vulnerabilities in our…
Content Type: Press release
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
December 21, 2018
CONTACTS:
Alex Betschen, Civil Liberties & Transparency Clinic, [email protected], 716–531–6649
Colton Kells, Civil Liberties & Transparency Clinic, [email protected], 585–766–5119
Abdullah Hasan, ACLU, [email protected], 646–905–8879
NEW YORK — Privacy International, the American Civil Liberties Union, and the Civil Liberties & Transparency Clinic of the University at Buffalo School of Law filed a lawsuit today…
Content Type: News & Analysis
This piece was originally published on Just Security.
Ten years ago, an FBI official impersonated an Associated Press reporter to lure and track a teenager suspected of sending in prank bomb threats to his school. To find him, the FBI agent, posing as a reporter, sent the teenager links to a supposed story he was working on, but the links were infested with malware that once clicked on quickly exposed the teen’s location. More recently, the FBI has seized and modified websites so…
Content Type: Press release
In a remarkable development in Privacy International's four year legal battle against the UK Government's powers to hack phones and computers on a massive scale, the UK Supreme Court has agreed to hear the London-based charity's case in December 2018.
Privacy International's case stems from a decision by the Investigatory Powers Tribunal (a specialised court set up to hear complaints against government surveillance, including surveillance carried out by the UK intelligence agencies) finding…
Content Type: Advocacy
This report sheds light on the current state of affairs in data retention regulation across the EU post the Tele-2/Watson judgment. Privacy International has consulted with digital rights NGOs and industry from across the European Union to survey 21 national jurisdictions (Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and the United…
Content Type: Long Read
Introduction
A growing number of governments around the world are embracing hacking to facilitate their surveillance activities. Yet hacking presents unique and grave threats to our privacy and security. It is far more intrusive than any other surveillance technique, capable of accessing information sufficient to build a detailed profile of a person, as well as altering or deleting that information. At the same time, hacking not only undermines the security of targeted systems, but also has…
Content Type: Long Read
This piece was orignally published in Slate in February 2017
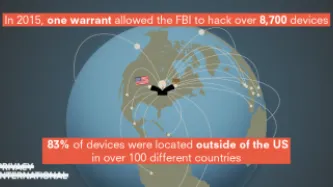
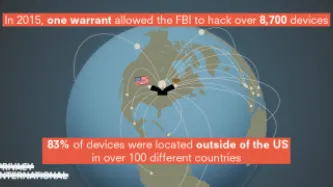
In 2015, the FBI obtained a warrant to hack the devices of every visitor to a child pornography website. On the basis of this single warrant, the FBI ultimately hacked more than 8,700 computers, resulting in a wave of federal prosecutions. The vast majority of these devices—over 83 percent—were located outside the United States, in more than 100 different countries. Now, we are in the midst of the first cases…
Content Type: Press release
Today, Privacy International, together with five internet and communications providers from around the world, have lodged an application before the European Court of Human Rights to challenge the British Government's use of bulk hacking abroad. Until we brought our original case at the Investigatory Powers Tribunal (IPT) in 2014, the Government had never admitted that it engaged in hacking. Now we are learning for the first time how far-reaching the Government's global hacking capabilities are…
Content Type: Press release
Privacy International General Counsel Caroline Wilson Palow said
"Today's opinion issued by the Advocate General of the European Court of Justice (ECJ) is a serious blow to the UK's Investigatory Powers Bill (IPBill). It, hopefully, presages a strong judgment from the Court itself.
The bulk powers - what we would call mass surveillance powers - embedded throughout the IPBill go far beyond tackling serious crime. They would give a range of public bodies, not just the Police and…
Content Type: Long Read
This piece originally appeared here.
On both sides of the Atlantic, we are witnessing the dramatic expansion of government hacking powers. In the United States, a proposed amendment to Rule 41 of the Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure would permit the government to obtain a warrant, in certain circumstances, to hack unspecified numbers of electronic devices anywhere in the world. Meanwhile, across the pond, the British Parliament is currently debating the Investigatory…