Search
Content type: Examples
On March 19, the Peruvian government instituted a daily curfew from 8pm to 5am, which applies to all but those working to provide essential services. Members of the print and broadcast press must carry their special permits, badges, and ID cards, and those requiring urgent medical care are allowed to travel. Private citizens are no longer allowed to drive their own cars at any time except where necessary for the above groups. The law is being enforced by the police and armed forces.
Sources:…
Content type: Examples
To contain the coronavirus, Vietnam focused on aggressive contact tracing, forced quarantines for all people arriving in the country, cancelling all foreign flights, conscripting medical students and retired doctors and nurses, instituting surveillance, and mobilising medical and military personnel as well as its national network of informants. As of March 24, the country had reported 123 confirmed cases and no deaths; as of March 20 the country had tested 15,637 people. About 800 people have…
Content type: Examples
The US Department of Justice has asked Congress for the ability to ask chief judges to detain people indefinitely without trial during emergencies as one of a number of new powers the department is seeking during the coronavirus crisis. The DoJ also wants Congress to pause the statute of limitations for criminal investigations during national emergencies and for one year following their end, and wishes to change the Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure in some cases to expand the use of…
Content type: Examples
The new Singaporean app, TraceTogether, developed by the Government Technology Agency in collaboration with the Ministry of Health was launched on March 20 after eight weeks of development. The app, which can be downloaded by anyone with a Singapore mobile number and a Bluetooth-enabled smartphone, asks users to turn on Bluetooth and location services, and enable push notifications. The app works by exchanging short-distance Bluetooth signals between phones to detect other users within two…
Content type: Examples
Technology such as Hong Kong's electronic monitoring bracelets, used to ensure that people do not break their mandated quarantine, may appear reasonable during a pandemic, but could be problematic if deployed widely and used to identify those who have joined anti-government protests. The same applies to emergency legislation such as that passed by the UK government granting the government extraordinary new powers to shut down airports and ban gatherings. History provides examples:…
Content type: Examples
The Greek government issued a ban on all unnecessary traffic from March 23 to April 6 in order to stop the spread of the coronavirus. Anyone moving around under one of the list of exceptions must carry a police identity card or passport and a certificate of movement, which citizens obtain by filling out an online form (at form.gov.gr), or by filling out a paper form listing the reason for leaving home, or by sending an SMS. Employees are issued a certificate by their employer. The government…
Content type: Advocacy
The letter has been signed by more than 40 organisations and it is open for individuals to sign.
At the moment, the Department of Health and Social Care has given no assurance that NHS data will not be shared with the Home Office and used for immigration enforcement, including for those people with a confirmed coronavirus diagnosis.
Assurances which were confirmed by the Irish government as part of their response to COVID-19: last week, during a Parliamentary debate, Irish Minister of Health…
Content type: Examples
Russia has set up a coronavirus information centre to to monitor social media for misinformation about the coronavirus and spot empty supermarket shelves using a combination of surveillance cameras and AI. The centre also has a database of contacts and places of work for 95% of those under mandatory quarantine after returning from countries where the virus is active. Sherbank, Russia's biggest bank, has agreed to pay for a free app that will provide free telemedicine consultations.
Source:…
Content type: Examples
Hong Kong is issuing electronic tracker wristbands to people under compulsory home quarantine to ensure they do not go out. The wristbands are accompanied by a mandatory smartphone app that shares their location with the government via messaging platforms such as WeChat and WhatsApp. Upon arriving at the place where they are quarantined, users walk around the corners so the technology can track the space in which they are confined.
Source: https://www.cnbc.com/2020/03/18/hong-kong-uses-…
Content type: Examples
The Serb-dominated Republika Srpska, one of two entities that make up Bosnia and Herzegovina, is introducing fines of €500 to €1,500 (individuals) or €3,000 to €9,000 for spreading "panic and disorder" by publishing false news about the coronavirus outbreak in the media and on social networks.
Source: https://balkaninsight.com/2020/03/19/bosnias-republika-srpska-imposes-fines-for-coronavirus-fake-news/
Writer: Danijel Kovacevic
Publication: BalkanInsight
Content type: Examples
The Paraguayan Minister of Defense, Bernardino Soto Estigarribia, announced that from March 17 onward restrictions on movement and crowds would be enforced by the military along with the police forces. The minister said it should not be thought of as a violation of human rights because the military understand the importance of respect. The country declared a state of emergency on March 16.
Source: https://www.ultimahora.com/covid-19-militares-tambien-controlaran-circulacion-personas-…
Content type: Examples
The presidential decree declaring a health emergency in Paraguay empowers the Ministry of Public Health to order "general preventive isolation" from 8:00 p.m. to 4:00 a.m, with exceptions for those doing vital work such as delivering food or transportation. The Ministry of the Interior and its police forces patrol the streets to enforce the measures.
Sources:
https://news.yahoo.com/military-roadblocks-curfews-latin-america-023213811.html
https://www.presidencia.gov.py/archivos/documentos/…
Content type: Video
You’re a witness or a victim or a suspect of a crime; or even just travelling going on holiday. Officials demand your phone, then disappear with it. What happened to your phone? What happened to your data? What will happen to you?
We all generate vast amounts of data using our mobile phones - more than most of us are aware of - and that data has become increasingly attractive to law enforcement agencies around the world, enabled by ‘extraction technologies’ supplied by companies like…
Content type: Advocacy
In December 2019 Privacy International made submissions to Police Scotland in relation to documents designed to explain to the public how cyber kiosks will work and what information will be given to victims when Police Scotland extract data from their phone.
Police Scotland rely on 'consent' to seize a phone from a victim. We believe the lack of information provided to the individual regarding extraction, examination, retention, deletion, sharing and search parameters undermines that any…
Content type: News & Analysis
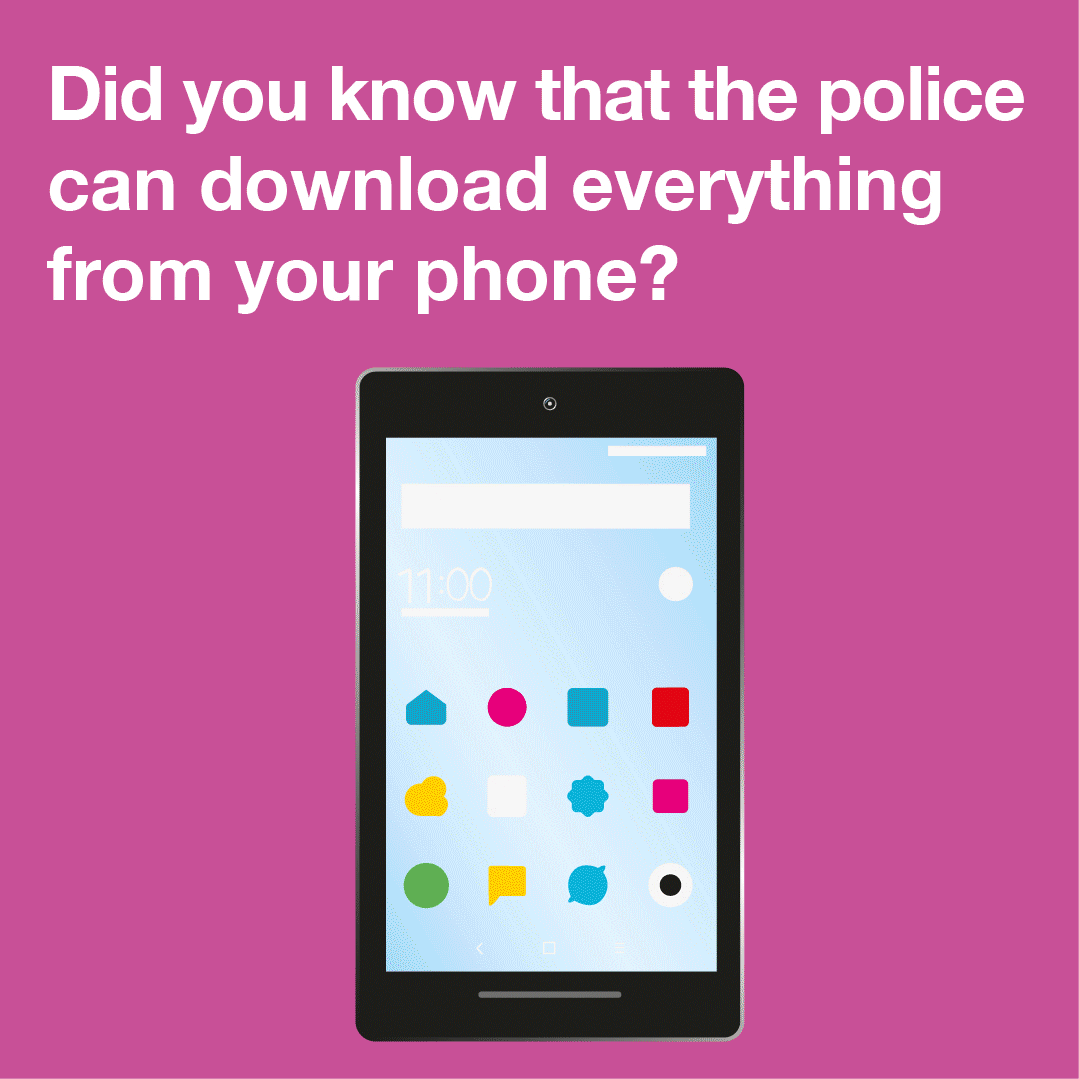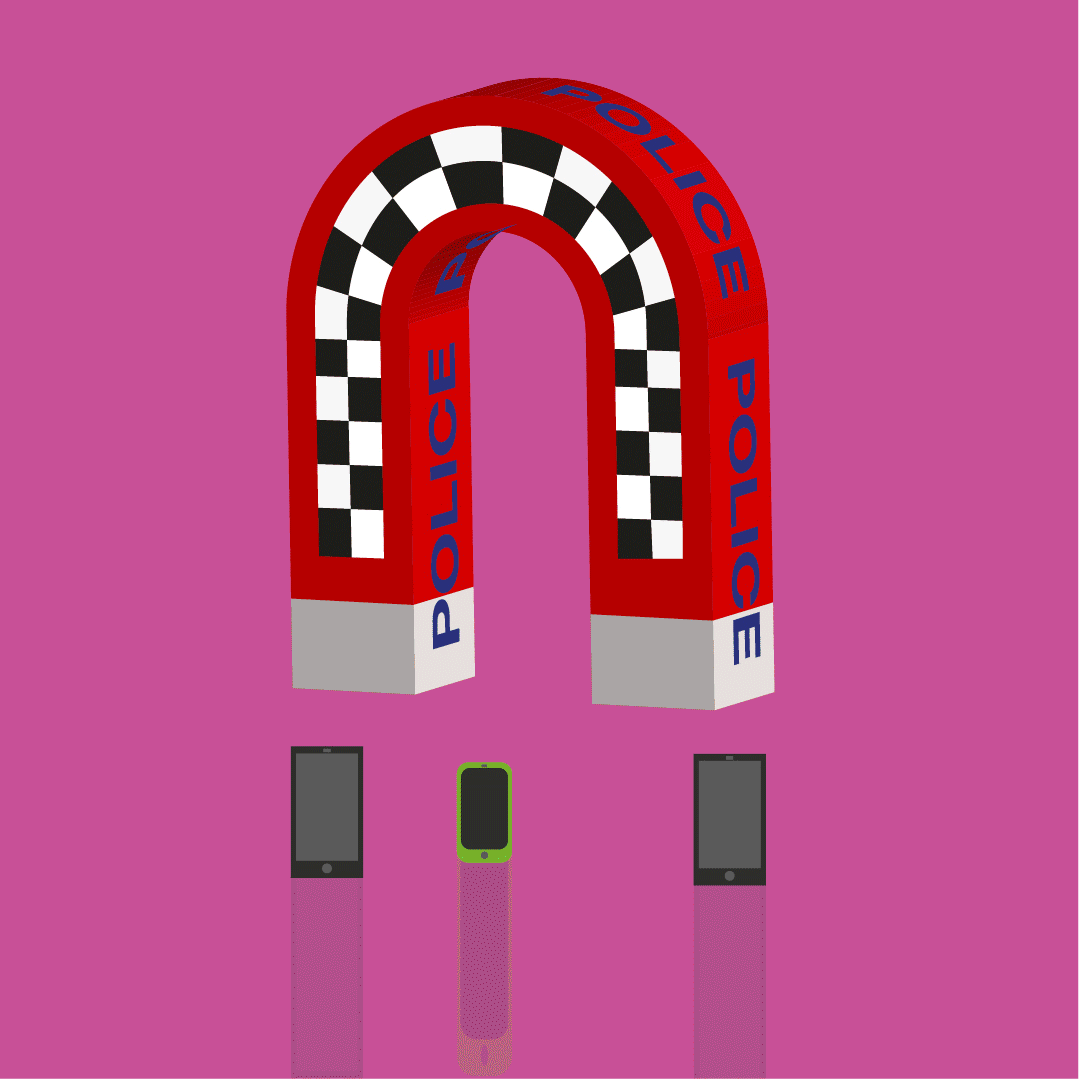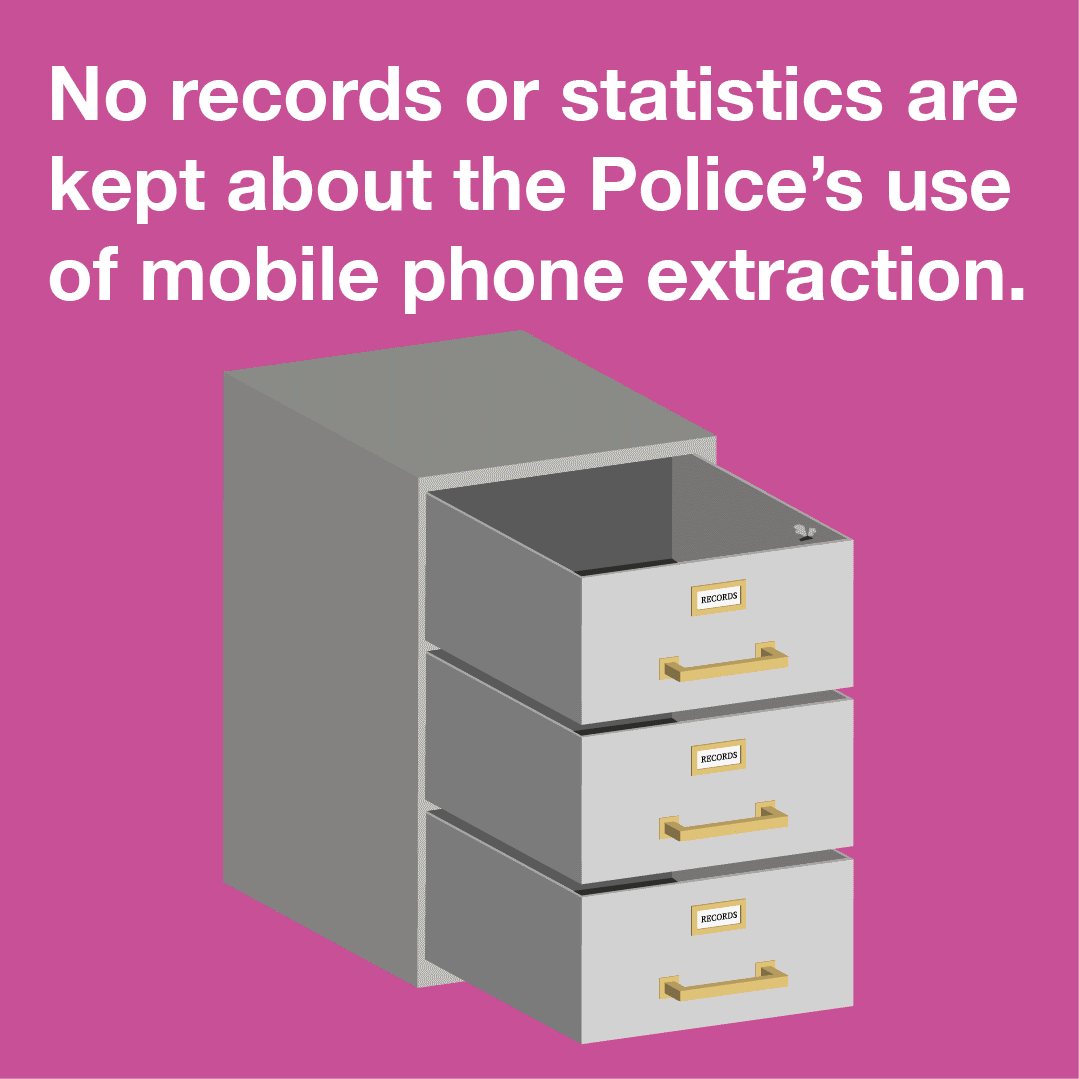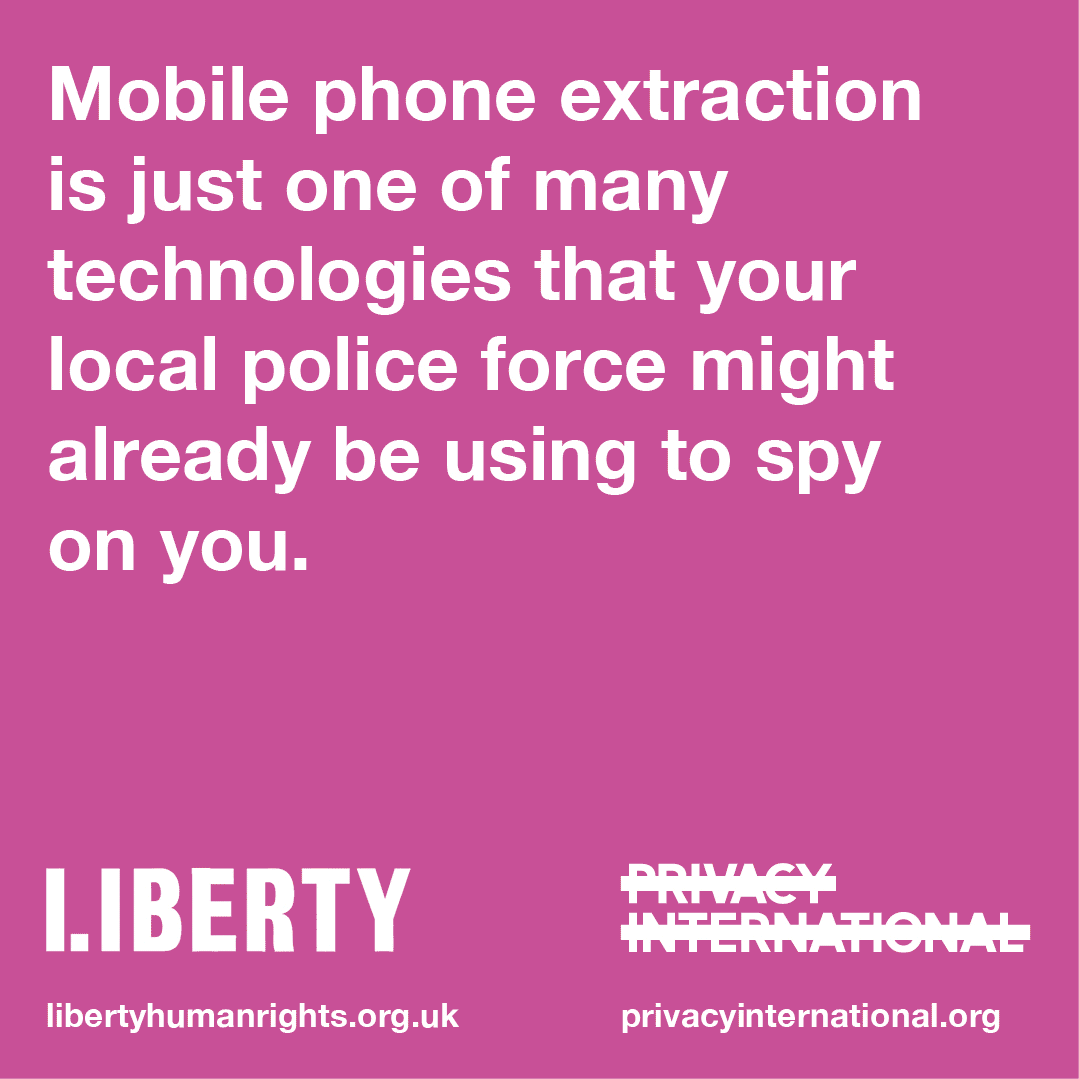
In the last few months strong concerns have been raised in the UK about how police use of mobile phone extraction dissuades rape survivors from handing over their devices: according to a Cabinet Office report leaked to the Guardian, almost half of rape victims are dropping out of investigations even when a suspect has been identified. The length of time it takes to conduct extractions (with victims paying bills whilst the phone is with the police) and the volume of data obtained by the…
Content type: Long Read
In this piece we examine mobile phone extraction, relying on publicly available information and Privacy International’s experience from conducting mobile phone extraction using a Cellebrite UFED Touch 2. We welcome input from experts in the field. This is a rapidly developing area. Just as new security features are announced for phones, so too new methods to extract data are found.
[All references can be found in the pdf version below.]
General explanation of mobile phone…
Content type: Report
“...a mobile device is now a huge repository of sensitive data, which could provide a wealth of information about its owner. This has in turn led to the evolution of mobile device forensics, a branch of digital forensics, which deals with retrieving data from a mobile device.”
The situation in Scotland regarding the use of mobile phone extraction has come a long way since the secret trials were exposed. The inquiry by the Justice Sub-Committee, commenced on 10 May 2018, has brought much…
Content type: Examples
In 2018, Brian Hofer, the chair of Oakland's Privacy Advisory Commission, filed suit after police wrongfully stopped him at gunpoint because their automated license plate recognition system, supplied by Vigilant Solutions, indicated that the rental car he was driving had been stolen. The car had in fact been stolen some months earlier, but been recovered. Despite such errors, police claim that the technology has helped reduce crime, identify stolen vehicles, and identify and arrest suspects.…
Content type: Examples
In February 2019 Gemalto announced it would supply the Uganda Police Force with its Cogent Automated Biometric Identification System and LiveScan technology in order to improve crime-solving. LiveScan enables police to capture biometric data alongside mugshots and biographical data. CABIS speeds up the biometric matching process by mapping distinctive characteristics in fingerprints, palm prints, and facial images. The Ugandan police will also pilot Gemalto's Mobile Biometric Identification…
Content type: Examples
In February 2019 BuzzFeed News reported that one of the largest home DNA testing companies, FamilyTreeDNA, had formed an agreement with the FBI to grant the agency access to its database of more than 1 million genetic profiles, most of which were supplied by consumers with no thought that they would be accessible to law enforcement. FamilyTreeDNA has also agreed to test DNA evidence and identify remains of victims of violent crimes for the FBI in its own laboratory. FamilyTreeDNA said…
Content type: Examples
In February 2019, the city of Rio de Janeiro announced that its police security operation for the annual five-day Carnival would include facial recognition and vehicle license plate cameras to identify wanted individuals and cars. Municipal officials said the system would help reduce thefts and robberies; critics dissented on the basis that a period when people are wearing masks, heavy makeup, glitter, and costumes is a bad time to test the technology.
https://riotimesonline.com/brazil-news/…
Content type: Examples
VeriPol, a system developed at the UK's Cardiff University, analyses the wording of victim statements in order to help police identify fake reports. By January 2019, VeriPol was in use by Spanish police, who said it helped them identify 64 false reports in one week and was successful in more than 80% of cases. The basic claim is that AI can find patterns that are common to false statements; among the giveaways experts say that false statements are likely to be shorter than genuine ones, focus…
Content type: Examples
In November 2016 the UK Information Commissioner's Office issued an enforcement notice against London's Metropolitan Police, finding that there had been multiple and serious breaches of data protection law in the organisation's use of the Gangs Violence Matrix, which it had operated since 2012. The ICO documented failures of oversight and coherent guidance, and an absence of basic data protection practices such as encryption and agreements covering data sharing. Individuals whose details are…
Content type: Explainer
We look at the recently published report on forensic science in the UK, highlight concerns about police not understanding new tech used to extract data from mobile phones; the risk of making incorrect inferences and the general lack of understanding about the capabilities of these tools.
The delivery of justice depends on the integrity and accuracy of evidence and trust that society has in it. So starts the damning report of the House of Lords Science and Technology Select…
Content type: News & Analysis
US Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), the agency at the centre of carrying out President Trump’s “zero tolerance” approach to immigration enforcement and family separation, has for years been contracting a US surveillance company to intercept peoples’ communications across the United States. The wide potential scope for the use of the powers raises concerns about their use for the real-time surveillance of people, families, and communities caught up in Trump’s immigration crackdown…
Content type: Long Read
Imagine that every time you want to attend a march, religious event, political meeting, protest, or public rally, you must share deeply personal information with police and intelligence agencies, even when they have no reason to suspect you of wrongdoing.
First, you need to go to the police to register; have your photo taken for a biometric database; share the contacts of your family, friends, and colleagues; disclose your finances, health records, lifestyle choices, relationship status, and…
Content type: News & Analysis
A mobile device is a huge repository of sensitive data, which could provide a wealth of information about its owner and many others with whom the user interacts.
Companies like Cellebrite, MSAB and Oxygen Forensics sell software and hardware to law enforcement. Once your phone is connected to one of these mobile phone extraction tools, the device extracts, analyses and presents the data contained on the phone.
What data these tools can extract and what method is used will…
Content type: Long Read
(In order to click the hyperlinks in the explainer below, please download the pdf version at the bottom of the page).
Content type: Explainer graphic
You can also read a more detailed explainer about mobile phone extraction here.
Content type: Examples
In 2018 a report from the Royal United Services Institute found that UK police were testing automated facial recognition, crime location prediction, and decision-making systems but offering little transparency in evaluating them. An automated facial recognition system trialled by the South Wales Police incorrectly identified 2,279 of 2,470 potential matches. In London, where the Metropolitan Police used facial recognition systems at the Notting Hill Carnival, in 2017 the system was wrong 98% of…