Search
Content type: News & Analysis
Unwanted Witness’ research into Safeboda highlighted the company’s failure to comply with some of the law's core data protection principles, with a number of implications for the exercise of data subject rights. The enforcement action against Safeboda by National Information Technology Authority, Uganda (NITA-U) requires the company to make fundamental changes to how they handle people's personal data in order to comply with the Data Protection and Privacy Act, 2019.
This first landmark…
Content type: Long Read
What’s the ruling all about?The Constitutional Court of South Africa in a historic judgment declared that bulk interception by the South African National Communications Centre is unlawful and invalid. Furthermore, the Constitutional Court found that the Regulation of Interception of Communications and Provision of Communication-Related Information Act (RICA) 1) was deficient in failing to provide at least a post-notification procedure for subjects of interception; 2) failed to ensure the…
Content type: News & Analysis
Today, the Constitutional Court of South Africa in a historic judgment declared that bulk interception by the South African National Communications Centre is unlawful and invalid.
The judgment is a confirmation of the High Court of South Africa in Pretoria’s powerful rejection of years of secret and unchecked surveillance by South African authorities against millions of people - irrespective of whether they reside in South Africa.
The case was brought by two applicants, the amaBhungane Centre…
Content type: News & Analysis
Today, the UK High Court has quashed a decision by the Investigatory Powers Tribunal (IPT) and held that section 5 of the Intelligence Services Act (ISA) 1994 does not permit the issue of general warrants to authorise property interference and certain forms of computer hacking.
The Court referred to cases dating back to the 18th century, which demonstrate the common law’s insistence that the Government cannot search private premises without lawful authority even in the national security…
Content type: News & Analysis
Privacy International (PI) welcomes today's report from the UK Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) into three credit reference agencies (CRAs) which also operate as data brokers for direct marketing purposes. As a result, the ICO has ordered the credit reference agency Experian to make fundamental changes to how it handles people's personal data within its offline direct marketing services.
It is a long overdue enforcement action against Experian.…
Content type: Long Read
Content type: Long Read
Q&A: EU's top court rules that UK, French and Belgian mass surveillance regimes must respect privacy
Content type: Long Read
An edited version of this article was originally published on the EDRi website in September 2020.
Introduction
Monopolies, mergers and acquisitions, anti-trust laws. These may seem like tangential or irrelevant issues for privacy and digital rights organisations. But having run our first public petition opposing a big tech merger, we wanted to set out why we think this is an important frontier for people's rights across Europe and indeed across the world.
In June, Google notified the…
Content type: News & Analysis
Back in January, Privacy International and over 50 other organisations wrote to Google asking the company to take action over pre-installed apps that cannot be deleted (often known as “bloatware”), which can leave users vulnerable to their data being collected, shared and exposed without their knowledge or consent. Thousands of people from over 50 countries signed our petition supporting this ask. We welcome the constructive conversations we had with Google following this campaign and for the…
Content type: News & Analysis
No doubt this is turning out to be a summer full of news about internet companies' digital dominance.
In June, Google notified the European Commission of its plan to acquire Fitbit - a plan that we immediately identified would raise grave concerns for our well-being as consumers.
Today the European Commission has made its decision. And it's good news.
The European regulator has decided to undertake a detailed 'Phase 2' investigation, rather than just green light Google's plans, voicing also the…
Content type: News & Analysis
In September 2019, PI published the report Your Mental Health for Sale. Our investigation looked into popular mental health websites and their data sharing practices.
Our findings suggest that, at the time of the research, most websites we looked at were using third party tracking for advertising purposes, sometimes relying on programmatic advertising technologies such as Real Time Bidding (RTB), sharing personal data with potentially thousands of actors. Some websites were also found sharing…
Content type: News & Analysis
At a time where the mass surveillance of protests has been at the forefront, the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights released a timely report on the impact of new technologies on the promotion and protection of human rights in the context of assemblies, including peaceful protests.
The new report highlights the strong ties between protest and privacy and warns that “…the use of some such technologies to surveil or crack down on protesters can lead to human rights violations, including…
Content type: Case Study
The Ugandan government has a running contract with the Chinese tech giant, Huawei, to supply and install CCTV cameras along major highways within the capital, Kampala, and other cities.
While details of the contract remain concealed from the public, the Uganda Police Force (UPF) released a statement, simply confirming its existing business partnership for telecommunication and surveillance hardware, and software between the security force and Huawei. However, it is not clear whether the…
Content type: Long Read
Introduction
In August 2019, when Facebook announced a few new features for advertisers such as ads in search, PI decided to take an in-depth look at what features the company offers its users when it comes to understanding its advertising practices. One of these features, which caught our attention is Facebook Ads Preference, a tool that among other things, lists businesses/advertisers that have uploaded your personal data to target you with (or exclude you from) ads on the platform.
Content type: Long Read
This article has been written by our partner organisation InternetLab. Read this article in Portuguese here.
Over the last months, the organisation InternetLab has researched privacy, data protection, gender, and social protection, focusing on the beneficiaries of the Bolsa Familia Program (PBF). The PBF is the most extensive Brazilian cash transfer program, and its functioning is linked to CadÚnico, a database that comprises 40% of the country’s population. Moreover, it is a program whose…
Content type: News & Analysis
Almost a year and a half ago we complained about seven companies to three data protection authorities in Europe. These companies, ranging from AdTech to data brokers and credit rating agencies, thrive on the collection, exploitation and processing of personal data. They profile and categorise people - without our knowledge and infringing multiple legal requirements.
Now, the French Data Protection Authority CNIL has informed us that they are following the same route and …
Content type: News & Analysis
This piece was originally published by Unwanted Witness here.
Today marks exactly one year since Uganda passed its data protection law, becoming the first East African country to recognize privacy as a fundamental human right, as enshrined in Art 27 of the 1995 Uganda Constitution as well as in regional and International laws.
The Data Protection and Privacy Act, 2019 aims to protect individuals and their personal data by regulating processing of personal information by state and non-state…
Content type: Long Read
Background
Kenya’s National Integrated Identity Management Scheme (NIIMS) is a biometric database of the Kenyan population, that will eventually be used to give every person in the country a unique “Huduma Namba” for accessing services. This system has the aim of being the “single point of truth”, a biometric population register of every citizen and resident in the country, that then links to multiple databases across government and, potentially, the private sector.
NIIMS was introduced…
Content type: Long Read
This piece was written by Aayush Rathi and Ambika Tandon, who are policy officers at the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS) in India. The piece was originally published on the website Economic Policy Weekly India here.
In order to bring out certain conceptual and procedural problems with health monitoring in the Indian context, this article posits health monitoring as surveillance and not merely as a “data problem.” Casting a critical feminist lens, the historicity of surveillance practices…
Content type: Report
The changes discussed in this article are based on a second analysis performed in late November, 3 months after the original study Your Mental Health is for Sale and following the exact same methodology. All data collected can be found at the bottom of this page.
Change is possible
Back in September 2019 we published the report Your Mental Health is for Sale exposing how a majority of the top websites related to mental health in France, Germany and the UK share data for advertising purposes.…
Content type: News & Analysis
On 30 January 2020, Kenya’s High Court handed down its judgment on the validity of the implementation of the National Integrated Identity Management System (NIIMS), known as the Huduma Namba. Privacy International submitted an expert witness testimony in the case. We await the final text of the judgment, but the summaries presented by the judges in Court outline the key findings of the Court. Whilst there is much there that is disappointing, the Court found that the implementation of NIIMS…
Content type: Advocacy
We welcome the effort by the Government of Kenya to give life to and specify the right to privacy, already enshrined in Article 31(c) and (d) of the Constitution of Kenya by proposing a draft Data Protection Act. We particularly appreciate the direct reference to this Constitutional right in the purpose of the Act and the way it is referred to on several occasions in the Act.
While these efforts have positive intentions and we are pleased that Kenya has adopted a comprehensive data protection…
Content type: News & Analysis
Today Advocate General (AG) Campos Sánchez-Bordona of the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU), issued his opinions (C-623/17, C-511/18 and C-512/18 and C-520/18) on how he believes the Court should rule on vital questions relating to the conditions under which security and intelligence agencies in the UK, France and Belgium could have access to communications data retained by telecommunications providers.
The AG addressed two major questions:
(1) When states seek to impose…
Content type: Advocacy
As any data protection lawyer and privacy activist will attest, there’s nothing like a well-designed and enforced data protection law to keep the totalitarian tendencies of modern Big Brother in check.
While the EU’s data protection rules aren’t perfect, they at least provide some limits over how far EU bodies, governments and corporations can go when they decide to spy on people.
This is something the bloc’s border control agency, Frontex, learned recently after coming up with a plan to…
Content type: Long Read
The pressing need to fix our cybersecurity (mis)understandings
Despite all the efforts made so far by different, cybersecurity remains a disputed concept. Some states are still approving cybersecurity laws as an excuse to increase their surveillance powers. Despite cybersecurity and cybercrime being different concepts, the confusion between them and the broad application of criminal statutes is still leading to the criminalise legitimate behaviour.
All of this represents a sizable challenge…
Content type: Long Read
Photo by Nadine Shaabana on Unsplash
Digital identity providers
Around the world, we are seeing the growth of digital IDs, and companies looking to offer ways for people to prove their identity online and off. The UK is no exception; indeed, the trade body for the UK tech industry is calling for the development of a “digital identity ecosystem”, with private companies providing a key role. Having a role for private companies in this sector is not necessarily a problem: after all, …
Content type: News & Analysis
Today, the High Court of South Africa in Pretoria in a historic decision declared that bulk interception by the South African National Communications Centre is unlawful and invalid.
The judgment is a powerful rejection of years of secret and unchecked surveillance by South African authorities against millions of people - irrespective of whether they reside in South Africa.
The case was brought by two applicants, the amaBhungane Centre for Investigative Journalism and journalist Stephen…
Content type: Long Read
In December 2018, Privacy international exposed the dubious practices of some of the most popular apps in the world.Out of the 36 apps we tested, we found that 61% automatically transfer data to Facebook the moment a user opens the app. This happens whether the user has a Facebook account or not, and whether they are logged into Facebook or not. We also found that some of those apps routinely send Facebook incredibly detailed and sometimes sensitive personal data. Again, it didn’t matter if…
Content type: News & Analysis
The Watson/Tele2 decision of the CJEU concerned section 1 and 2 of DRIPA and the Data Retention Regulations 2014. This contained the legislative scheme concerning the power of the Secretary of State to require communications service providers to retain communications data. Part 3 of the Counter-Terrorism and Security Act 2015 amended DRIPA so that an additional category of data - that necessary to resolve Internet Protocol addresses - could be included in a requirement to retain…
Content type: Long Read
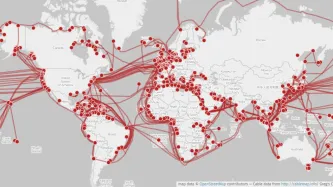
Six years after NSA contractor Edward Snowden leaked documents providing details about how states' mass surveillance programmes function, two states – the UK and South Africa – publicly admit using bulk interception capabilities.Both governments have been conducting bulk interception of internet traffic by tapping undersea fibre optic cables landing in the UK and South Africa respectively in secret for years.Both admissions came during and as a result of legal proceedings brought by Privacy…