Search
Content type: Advocacy
BackgroundThe Snowden revelations and subsequent litigation have repeatedly identified unlawful state surveillance by UK agencies. In response, the UK Parliament passed the highly controversial Investigatory Powers Act 2016 (IPA), which authorised massive, suspicionless surveillance on a scale never seen before, with insufficient safeguards or independent oversight.Privacy International led legal challenges to this mass surveillance regime both before and after the Act became law. The Act…
Content type: Report
This policy paper seeks to determine the potential for the existing international private military and security companies (PMSCs) regulatory framework to support more effective regulation of surveillance services provided by the private sector.In order to achieve this, and given that this paper addresses an issue that is at the intersection of two domains, it seeks to establish a common language and terminology between security sector governance and surveillance practitioners.In…
Content type: News & Analysis
As Amnesty International and Forbidden Stories continue to publish crucial information about the potential targets of NSO Group’s spyware, we know this much already: something needs to be done.
But what exactly needs to be done is less obvious. Even though this is not the first time that the world has learned about major abuses by the surveillance industry (indeed, it’s not even the first time this month), it’s difficult to know what needs to change.
So how can the proliferation and use of…
Content type: Press release
Today, the ICO has issued a long-awaited and critical report on Police practices regarding extraction of data from people's phones, including phones belonging to the victims of crime.
The report highlights numerous risks and failures by the police in terms of data protection and privacy rights. The report comes as a result of PI’s complaint, dating back to 2018, where we outlined our concerns about this intrusive practice, which involves extraction of data from devices of victims, witnesses…
Content type: News & Analysis
In mid-2019, MI5 admitted, during a case brought by Liberty, that personal data was being held in “ungoverned spaces”. Much about these ‘ungoverned spaces’, and how they would effectively be “governed” in the future, remained unclear. At the moment, they are understood to be a ‘technical environment’ where personal data of unknown numbers of individuals was being ‘handled’. The use of ‘technical environment’ suggests something more than simply a compilation of a few datasets or databases.
The…
Content type: News & Analysis
Today Advocate General (AG) Campos Sánchez-Bordona of the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU), issued his opinions (C-623/17, C-511/18 and C-512/18 and C-520/18) on how he believes the Court should rule on vital questions relating to the conditions under which security and intelligence agencies in the UK, France and Belgium could have access to communications data retained by telecommunications providers.
The AG addressed two major questions:
(1) When states seek to impose…
Content type: Case Study
On 3 December 2015, four masked men in plainclothes arrested Isnina Musa Sheikh in broad daylight (at around 1 p.m.) as she served customers at her food kiosk in Mandera town, in the North East of Kenya, Human Rights Watch reported. The men didn’t identify themselves but they were carrying pistols and M16 assault rifles, commonly used by Kenyan defence forces and the cars that took her away had their insignia on the doors. Isnina’s body was discovered three days later in a shallow grave about…
Content type: Case Study
The prohibition against torture is absolute. There are no exceptional circumstances whatsoever which can be used to justify torture.
And yet, torture is still being carried out by state officials around the world, driven by states’ ability to surveil dissidents, and intercept their communications.
In 2007, French technology firm Amesys (a subsidiary of Bull) supplied sophisticated communications surveillance systems to the Libyan intelligence services. The systems allegedly permitted the…
Content type: Long Read
Six years after NSA contractor Edward Snowden leaked documents providing details about how states' mass surveillance programmes function, two states – the UK and South Africa – publicly admit using bulk interception capabilities.Both governments have been conducting bulk interception of internet traffic by tapping undersea fibre optic cables landing in the UK and South Africa respectively in secret for years.Both admissions came during and as a result of legal proceedings brought by Privacy…
Content type: Long Read
Imagine that every time you want to attend a march, religious event, political meeting, protest, or public rally, you must share deeply personal information with police and intelligence agencies, even when they have no reason to suspect you of wrongdoing.
First, you need to go to the police to register; have your photo taken for a biometric database; share the contacts of your family, friends, and colleagues; disclose your finances, health records, lifestyle choices, relationship status, and…
Content type: Impact Case Study
What is the problem
For over two decades we have been documenting an alarming use and spread of surveillance. It is no longer just the wars on terror or drugs or migration that is driving this trend. The management of health crises and distribution of welfare regularly are among others being used to justify this turn to increasingly invasive forms of surveillance. From country to country we see the same ideas and the same profiteers expanding their reach.
When we first released our report on…
Content type: Explainer
Phone networks are divided between two networks: the physical and the mobile. The physical runs on the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) that serves your home phone. Mobile networks are dominant in the age of communication and are used to relay mobile communications to the PSTN. The most prominent mobile networks are GSM networks (Global System for Mobile communications) and are what we use everyday to communicate with one another. Another system is known as CDMA (Code Division Multiple…
Content type: Explainer
Video surveillance technologies are deployed in public and private areas for monitoring purposes. Closed-circuit television (CCTV)– a connected network of stationary and mobile video cameras– is increasingly used in public areas, private businesses and public institutions such as schools and hospitals. Systems incorporating video surveillance technologies have far greater powers than simply what the camera sees. Biometric technologies use the transmitted video to profile, sort and identify…
Content type: Long Read
Privacy International is celebrating Data Privacy Week, where we’ll be talking about privacy and issues related to control, data protection, surveillance and identity. Join the conversation on Twitter using #dataprivacyweek.
Exercising the right to privacy extends to the ability of accessing and controlling our data and information, the way it is being handled, by whom, and for what purpose. This right is particularly important when it comes to control of how States perform these activities.…
Content type: News & Analysis
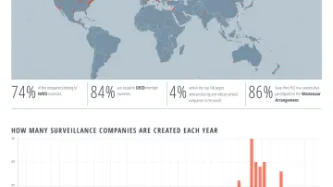
Privacy International is today proud to release the Surveillance Industry Index (SII), the world's largest publicly available educational resource of data and documents of its kind on the surveillance industry, and an accompanying report charting the growth of the industry and its current reach.
The SII, which is based on data collected by journalists, activists, and researchers across the world is the product of months of collaboration between Transparency Toolkit and Privacy…
Content type: Press release
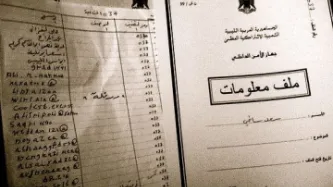
Privacy International today publishes a new investigation, based on exclusive documents, exposing the sale of European surveillance technologies to a secret unit of Egypt's intelligence infrastructure.
The Technical Research Department (TRD) is an independent unit within the General Intelligence Service (GIS), accountable only to the President. According to sources, the TRD has the biggest budget for surveillance technologies of any Egyptian government body. Such large public expenditure…
Content type: News & Analysis
Here are eight things we have learned from this week's hack of some 400GB of internal company material and correspondence from Italian surveillance company Hacking Team.
The Citizen Lab was right
The Citizen Lab, who in 2014 identified some 21 countries that are potential customers of Hacking Team, were right about all of them. A 2015 report stated that there was likely to be more. In fact, at least 45 countries are purchasers of Hacking Team's…
Content type: News & Analysis
There is a common practice within the surveillance industry that makes the already murky market even harder to track: collaborating companies.
Within Privacy International's Surveillance Industry Index there are 83 documents detailing collaborations between companies involved in developing and selling surveillance technologies. These documents represent a variety of relationships – some are friendly companies, others advertise corporate partners, and some present themselves as a distributor of…
Content type: News & Analysis
German surveillance technology company Trovicor played a central role in expanding the Ethiopian government's communications surveillance capacities, according to a joint investigation by Privacy International and netzpolitik.org.
The company, formerly part of Nokia Siemens Networks (NSN), provided equipment to Ethiopia's National Intelligence and Security Service (NISS) in 2011 and offered to massively expand the government's ability to intercept and store internet…
Content type: Press release
Governments across Central Asia have deployed advanced surveillance systems, including monitoring centres capable of spying on an entire country's communications, according to a new investigative report published today by Privacy International.
The comprehensive report, “Private Interests: Monitoring Central Asia”, contains personal accounts taken by Privacy International detailing how Central Asian governments use electronic surveillance technology to spy on activists and…
Content type: Press release
Privacy International, Reporters Without Borders, Digitale Gesellschaft, FIDH, and Human Rights Watch welcome news that the European Commission will move ahead and add specific forms of surveillance technology to the EU control list on dual use items, thus taking steps to finally hold companies to account who sell spy equipment and enable human rights abuses.
These important steps demonstrate that policymakers are beginning to wake up to the real harm that exists…
Content type: News & Analysis
Thousands of innocent people in London have had their communications spied on and collected through the use of invasive mobile phone surveillance technology, called IMSI Catchers, according to a recent report by the Times.
IMSI Catchers are no longer, and have not been for a while, a law enforcement secret. They have been featured crime dramas like the Wire and in movies such as Zero Dark Thirty. For years, the German Parliament has publicly received the number of IMSI Catcher…
Content type: News & Analysis
Global problems require global solutions. One of the significant emerging threats to human rights and democracy today is the incredible and mostly unaccountable spread of surveillance technologies.
The rapid proliferation of these systems has created a shadowy billion-dollar industry, where companies sell spying equipment with impunity to authoritarian regimes, who wield them against journalists, political activists, and human rights defenders.
Given the scale and international scope of this…
Content type: News & Analysis
Two new categories of surveillance systems were added into the dual-use goods and technologies control list of the Wassenaar Arrangement last week in Vienna, recognising for the first time the need to subject spying tools used by intelligence agencies and law enforcement to export controls.
While there are many questions that still need to be answered, Privacy International cautiously welcomes these additions to the Wassenaar Arrangement. Undoubtedly, these new…
Content type: News & Analysis
On at least two separate occasions, the South African government has provided funding to a well-resourced surveillance company for the development of mass surveillance technologies, the very equipment found to be used by the Gaddafi's repressive military regime in Libya, according to documents uncovered by Privacy International.
In February 2008, sandwiched between funding for a mechanical grape conveyor belt, and funding to improve gear changing and engine efficiency, the South African…
Content type: News & Analysis
Privacy International is pleased to announce the Surveillance Industry Index, the most comprehensive publicly available database on the private surveillance sector.
Over the last four years, Privacy International has been gathering information from various sources that details how the sector sells its technologies, what the technologies are capable of and in some cases, which governments a technology has been sold to. Through our collection of materials and brochures at surveillance trade…
Content type: News & Analysis
For some time now, Gamma International has been criticised for exporting dangerous surveillance technologies from the UK to repressive regimes. Now, we are learning that the company is taking its show on the road, as recent reports have said that Gamma are now attempting to export its products, including the spyware FinFisher, out of Switzerland.
With sales premises registered at a site just outside the Swiss capital Bern, Gamma has now applied to the Swiss Secretariat for…
Content type: News & Analysis
Through our Big Brother Incorporated project, Privacy International over the past two years has been campaigning against the export of surveillance technologies by Western companies to repressive regimes. One of the seminal moments of this campaign was in 2011, when we partnered with Wikileaks to release the SpyFiles, which catalogued hundreds of brochures, presentations, marketing videos, and technical specifications exposing the inner workings of the international trade in…
Content type: News & Analysis
Following reports that the Mexican prosecution authority appears to be not only using FinFisher, but also to be involved in a corruption scandal surrounding the purchase of this intrusive surveillance technology, the Mexican Permanent Commission (composed of members of the Mexican Senate and Congress) has urged Mexico's Federal Institute for Access to Public Information and Data Protection (IFAI) to investigate the use of spyware in Mexico.
The corruption scandal, which entails the…
Content type: Press release
The government today published a draft version of a bill that, if signed into law in its current form, would force Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and mobile phone network providers in Britain to install 'black boxes' in order to collect and store information on everyone's internet and phone activity, and give the police the ability to self-authorise access to this information. However, the Home Office failed to explain whether or not companies like Facebook, Google and Twitter will be…