Search
Content type: News & Analysis
The UK government has published a £20 million procurement for tech companies to provide live facial recognition technology (FRT) to police forces across the UK.Through BlueLight Commercial, a non-profit commercial consortium representing police and other emergency services, the government has issued a tender notice to establish a national multi-supplier framework for the provision of live FRT. The Scope of the framework is for “real-time deployment of facial recognition technology, which…
Content type: News & Analysis
Our mobile phones contain all kinds of data that ranges from photos, videos and emails to information about our health, the places we visit and our leisure time. This data is often relied upon by law enforcement authorities in criminal investigations.
Mobile phone extraction (MPE) tools are used for this purpose as they enable police and other authorities to download content and associated data from people’s phones. These tools are supplied by private companies to security forces and…
Content type: News & Analysis
What if we told you that every photo of you, your family, and your friends posted on your social media or even your blog could be copied and saved indefinitely in a database with billions of images of other people, by a company you've never heard of? And what if we told you that this mass surveillance database was pitched to law enforcement and private companies across the world?
This is more or less the business model and aspiration of Clearview AI, a company that only received worldwide…
Content type: News & Analysis
Around the world, we see migration authorities use technology to analyse the devices of asylum seekers. The UK via the Policing Bill includes immigration officers amongst those who can exercise powers to extract information from electronic devices. There are two overarching reasons why this is problematic:
The sole provision in the Policing Bill to extract information rests on voluntary provision and agreement, which fails to account for the power imbalance between individual and state. This…
Content type: News & Analysis
It is difficult to imagine a more intrusive invasion of privacy than the search of a personal or home computer ... when connected to the internet, computers serve as portals to an almost infinite amount of information that is shared between different users and is stored almost anywhere in the world.
R v Vu 2013 SCC 60, [2013] 3 SCR 657 at [40] and [41].
The controversial Police Crime Sentencing and Courts Bill includes provision for extracting data from electronic devices.
The Bill…
Content type: Press release
Privacy International (PI), together with Hermes Center for Transparency and Digital Human Rights, Homo Digitalis and noyb - the European Center for Digital Rights, has today filed a series of legal complaints against Clearview AI, Inc. The facial recognition company claims to have “the largest known database of 3+ billion facial images”. The complaints were submitted to data protection regulators in France, Austria, Italy, Greece and the United Kingdom.
As our complaints detail, Clearview AI…
Content type: News & Analysis
The Police, Crime, Sentencing and Courts (PCSC) Bill is currently being scrutinised by numerous civil society organisations such as Amnesty International UK and Liberty for its damaging impacts on peaceful protests, however it also contains important provisions regarding when, if and how the police and other governmental authorities can extract data from your phones and other electronic devices.
Chapter 3 of the PCSC Bill is a legislative response to the UK's Information Commissioner's Office…
Content type: News & Analysis
The College of Policing public consultation concerned the new Code of Practice in relation to the way information is managed and recorded in the Police National Computer (PNC), Police National Database (PND) and the forthcoming Law Enforcement Data Service (LEDS).
PI and Open Rights Group (ORG) believe that the way police records and information are managed, stored and disposed of can pose serious threats to privacy and other fundamental rights. Therefore they must not only be subject to strong…
Content type: News & Analysis
The Law Enforcement Data Service (LEDS) is a unified, common interface to a new mega-database currently being developed by the Home Office National Law Enforcement Data Programme (NLEDP). We believe that the development of the programme poses a threat to privacy and other rights and must be subjected to strong oversight, safeguards, and transparency measures.
As we explained in our analysis, the data in LEDS is vast, ever-increasing, worryingly mixes both evidential and intelligence material –…
Content type: Case Study
Facial recognition technology (FRT) is fairly present in our daily lives, as an authentication method to unlock phones for example. Despite having useful applications, FRT can also be just another technology used by those in power to undermine our democracies and carry out mass surveillance. The biometric data collected by FRT can be as uniquely identifying as a fingerprint or DNA. The use of this technology by third parties, specially without your consent, violates your right to privacy.
The…
Content type: Long Read
In April 2018, Amazon acquired “Ring”, a smart security device company best known for its video doorbell, which allows Ring users to see, talk to, and record people who come to their doorsteps.
What started out as a company pitch on Shark Tank in 2013, led to the $839 million deal, which has been crucial for Amazon to expand on their concept of the XXI century smart home. It’s not just about convenience anymore, interconnected sensors and algorithms promise protection and provide a feeling of…
Content type: Case Study
Well into the 21st century, Serbia still does not have a strong privacy culture, which has been left in the shadows of past regimes and widespread surveillance. Even today, direct police and security agencies’ access to communications metadata stored by mobile and internet operators makes mass surveillance possible.
However, a new threat to human rights and freedoms in Serbia has emerged. In early 2019, the Minister of Interior and the Police Director announced that Belgrade will receive “a…
Content type: News & Analysis
IMSI catchers (or stingrays as they are known in the US) are one of the surveillance technologies that has come to the forefront again in the protests against police brutality and systemic racism that have been sparked by the murder of George Floyd on 25 May 2020.
An International Mobile Subscriber Identity catcher – in short an “IMSI catcher” – is an intrusive piece of technology that can be used to locate and track all mobile phones that are switched on in a certain area. It does so by…
Content type: Press release
Today, the ICO has issued a long-awaited and critical report on Police practices regarding extraction of data from people's phones, including phones belonging to the victims of crime.
The report highlights numerous risks and failures by the police in terms of data protection and privacy rights. The report comes as a result of PI’s complaint, dating back to 2018, where we outlined our concerns about this intrusive practice, which involves extraction of data from devices of victims, witnesses…
Content type: News & Analysis
Yesterday, Amazon announced that they will be putting a one-year suspension on sales of its facial recognition software Rekognition to law enforcement. While Amazon’s move should be welcomed as a step towards sanctioning company opportunism at the expense of our fundamental freedoms, there is still a lot to be done.
The announcement speaks of just a one-year ban. What is Amazon exactly expecting to change within that one year? Is one year enough to make the technology to not discriminate…
Content type: News & Analysis
In a legal challenge brought by French activist group, La Quadrature du Net (LGDN), the Conseil d’État, the French highest court, has ruled that the use of drones by the police in the context of monitoring compliance with Covid-19 lockdown measures was unlawful.
The ruling found that the imagery and footage captured by drones flying at a low altitude was personal data to the extent that individuals filmed were identifiable. Consequently, the operation of drones by the police amounted…
Content type: Long Read
On 12 April 2020, citing confidential documents, the Guardian reported Palantir would be involved in a Covid-19 data project which "includes large volumes of data pertaining to individuals, including protected health information, Covid-19 test results, the contents of people’s calls to the NHS health advice line 111 and clinical information about those in intensive care".
It cited a Whitehall source "alarmed at the “unprecedented” amounts of confidential health information being swept up in the…
Content type: Press release
Photo by Ashkan Forouzani on Unsplash
Today Privacy International, Big Brother Watch, medConfidential, Foxglove, and Open Rights Group have sent Palantir 10 questions about their work with the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) during the Covid-19 public health crisis and have requested for the contract to be disclosed.
On its website Palantir says that the company has a “culture of open and critical discussion around the implications of [their] technology” but the company have so far…
Content type: Long Read
The UK’s Metropolitan Police have began formally deploying Live Facial Recognition technology across London, claiming that it will only be used to identify serious criminals on “bespoke ‘watch lists’” and on “small, targeted” areas.
Yet, at the same time, the UK’s largest police force is also listed as a collaborator in a UK government-funded research programme explicitly intended to "develop unconstrained face recognition technology", aimed “at making face…
Content type: News & Analysis
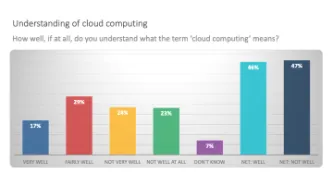
Cloud extraction allows law enforcement agencies to take huge amounts of your data from the Cloud via a legal back door. If law enforcement seize your phone or take it from a victim of crime, they can extract tokens or passwords from the device which lets them get access to data from apps such as Uber, Instagram, Slack, Gmail, Alexa and WhatsApp.
In so doing, law enforcement agencies can avoid official channels through cloud companies such as Google, Apple…
Content type: Press release
A large number of apps on smart phones store data in the cloud. Law enforcement can access these vast troves of data from devices and from popular apps with the push of a button using cloud extraction technology.
Mobile phones remain the most frequently used and most important digital source for law enforcement investigations. Yet it is not just what is physically stored on the phone that law enforcement are after, but what can be accessed from it, primarily data stored in the Cloud.…
Content type: News & Analysis
In the last few months strong concerns have been raised in the UK about how police use of mobile phone extraction dissuades rape survivors from handing over their devices: according to a Cabinet Office report leaked to the Guardian, almost half of rape victims are dropping out of investigations even when a suspect has been identified. The length of time it takes to conduct extractions (with victims paying bills whilst the phone is with the police) and the volume of data obtained by the…
Content type: Long Read
In this piece we examine mobile phone extraction, relying on publicly available information and Privacy International’s experience from conducting mobile phone extraction using a Cellebrite UFED Touch 2. We welcome input from experts in the field. This is a rapidly developing area. Just as new security features are announced for phones, so too new methods to extract data are found.
[All references can be found in the pdf version below.]
General explanation of mobile phone…
Content type: Long Read
Imagine that every time you want to attend a march, religious event, political meeting, protest, or public rally, you must share deeply personal information with police and intelligence agencies, even when they have no reason to suspect you of wrongdoing.
First, you need to go to the police to register; have your photo taken for a biometric database; share the contacts of your family, friends, and colleagues; disclose your finances, health records, lifestyle choices, relationship status, and…
Content type: News & Analysis
A mobile device is a huge repository of sensitive data, which could provide a wealth of information about its owner and many others with whom the user interacts.
Companies like Cellebrite, MSAB and Oxygen Forensics sell software and hardware to law enforcement. Once your phone is connected to one of these mobile phone extraction tools, the device extracts, analyses and presents the data contained on the phone.
What data these tools can extract and what method is used will…
Content type: News & Analysis
Protest movements throughout history have helped to shape the world we know today. From the suffragettes to the civil rights movement, and to contemporary movements such as those focusing on LGBTIQ+ rights, protests have become a vital way for many, who feel powerless otherwise, to have their voices heard.
But now, making the decision to attend a protest comes with consequences that you may very well be unaware of. This is because policing and security services, always hungry in their quest to…
Content type: Long Read
(In order to click the hyperlinks in the explainer below, please download the pdf version at the bottom of the page).
Content type: News & Analysis
Planning and participating in peaceful protests against governments or non-state actors’ policies and practices requires the capacity of individuals to communicate confidentially without unlawful interference. From protests in support of LGBTI rights to protests against specific projects that undermine local communities’ wellbeing, these movements would not have been possible without the ability to exchange ideas and develop plans in private spaces.
Unlawful interference with…
Content type: Long Read
The Privacy International Network is celebrating Data Privacy Week, where we’ll be talking about how trends in surveillance and data exploitation are increasingly affecting our right to privacy. Join the conversation on Twitter using #dataprivacyweek.
In the era of smart cities, the gap between the internet and the so-called physical world is closing. Gone are the days, when the internet was limited to your activities behind a desktop screen, when nobody knew you were a dog.
Today, the…