Search
Content type: Report
Over the past years, data retention regulation imposing generalised and indiscriminate data retention obligations to telecommunication companies and Internet service provides has been introduced in various jurisdictions across the world. As the data retention practices across the world have evolved this new report is an attempt to shed some light on the current state of affairs in data retention regulation across ten key jurisdictions. Privacy International has consulted with human…
Content type: Report
This policy paper seeks to determine the potential for the existing international private military and security companies (PMSC) regulatory framework to support more effective regulation of surveillance services provided by the private sector.In order to achieve this, and given that this paper addresses an issue that is at the intersection of two domains, it seeks to establish a common language and terminology between security sector governance and surveillance practitioners.In…
Content type: Long Read
The rise of the gig-economy, a way of working relying on short term contracts and temporary jobs rather than on an employed workforce, has enabled the growth of a number of companies over the last few years. But without the rights that comes with full employment, gig economy workers today don't have access to essential protections.
In 2021, PI worked with ACDU and Worker Info Exchange to shed a light on the power imbalance between workers and gig economy platforms, exposing how workers find…
Content type: Report
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) contributes significantly to security and privacy. For that reason, PI has long been in favour of the deployment of robust E2EE.Encryption is a way of securing digital communications using mathematical algorithms that protect the content of a communication while in transmission or storage. It has become essential to our modern digital communications, from personal emails to bank transactions. End-to-end encryption is a form of encryption that is even more private.…
Content type: Long Read
Introduction
In response to the unprecedented social, economic, and public health threats posed by the Covid-19 pandemic, the World Bank financed at least 232 "Covid-19 Response" projects. The projects were implemented across countries the World Bank classifies as middle and low-income.
This article will focus on eight (8) Covid-19 Response projects which sought to deliver social assistance to individuals and families on a "non-contributory" basis (this means that the intended beneficiaries…
Content type: Report
Privacy International’s submissions for the Independent Chief Inspector of Borders and Immigration inspection of the Home Office Satellite Tracking Service Programme
The Home Office have introduced 24/7 electronic monitoring and collection of the location data of migrants via GPS ankle tags. This seismic change cannot be overstated. The use of GPS tags and intention to use location data, kept for six years after the tag is removed, in immigration decision-making goes far beyond the mere…
Content type: Report
Human rights defenders across the world have been facing increasing threats and harms as result of the use of digital and technological tools used by governments and companies which enable the surveillance, monitoring and tracking of individuals and communities. They are continuously at risk of violence, intimidation and surveillance as a direct consequence of the work they do. Such surveillance has been shown to lead to arbitrary detention, sometimes to torture and possibly to extrajudicial…
Content type: Long Read
Tucked away in a discrete side street in Hungary’s capital, the European Union Agency for Law Enforcement Training (CEPOL) has since 2006 operated as an official EU agency responsible for developing, implementing, and coordinating training for law enforcement officials from across EU and non-EU countries.
Providing training to some 29,000 officials in 2018 alone, it has seen its budget rocket from €5 million in 2006 to over €9.3 million in 2019, and offers courses in everything from…
Content type: Report
“...a mobile device is now a huge repository of sensitive data, which could provide a wealth of information about its owner. This has in turn led to the evolution of mobile device forensics, a branch of digital forensics, which deals with retrieving data from a mobile device.”
The situation in Scotland regarding the use of mobile phone extraction has come a long way since the secret trials were exposed. The inquiry by the Justice Sub-Committee, commenced on 10 May 2018, has brought much…
Content type: Long Read
It is common ground that bulk collection of content would be a deprivation of the right to privacy. That is an inexcusable or unjustifiable step too far. Repeatedly the Government whether in litigation or legislating, has emphasised that they are not taking content in bulk. Content is the forbidden ground.
This has resulted in the Government seeking to explain, for example, what parts of an email would constitute content and meta data. Within the Investigatory Powers Act it has led to the…
Content type: Long Read
Six years after NSA contractor Edward Snowden leaked documents providing details about how states' mass surveillance programmes function, two states – the UK and South Africa – publicly admit using bulk interception capabilities.Both governments have been conducting bulk interception of internet traffic by tapping undersea fibre optic cables landing in the UK and South Africa respectively in secret for years.Both admissions came during and as a result of legal proceedings brought by Privacy…
Content type: Long Read
Imagine that every time you want to attend a march, religious event, political meeting, protest, or public rally, you must share deeply personal information with police and intelligence agencies, even when they have no reason to suspect you of wrongdoing.
First, you need to go to the police to register; have your photo taken for a biometric database; share the contacts of your family, friends, and colleagues; disclose your finances, health records, lifestyle choices, relationship status, and…
Content type: Long Read
Cellebrite, a surveillance firm marketing itself as the “global leader in digital intelligence”, is marketing its digital extraction devices at a new target: authorities interrogating people seeking asylum.
Israel-based Cellebrite, a subsidiary of Japan’s Sun Corporation, markets forensic tools which empower authorities to bypass passwords on digital devices, allowing them to download, analyse, and visualise data.
Its products are in wide use across the world: a 2019 marketing…
Content type: Long Read
The Privacy International Network is celebrating Data Privacy Week, where we’ll be talking about how trends in surveillance and data exploitation are increasingly affecting our right to privacy. Join the conversation on Twitter using #dataprivacyweek.
In the era of smart cities, the gap between the internet and the so-called physical world is closing. Gone are the days, when the internet was limited to your activities behind a desktop screen, when nobody knew you were a dog.
Today, the…
Content type: Long Read
The Privacy International Network is celebrating Data Privacy Week, where we’ll be talking about how trends in surveillance and data exploitation are increasingly affecting our right to privacy. Join the conversation on Twitter using #dataprivacyweek.
It is often communities who are already the most marginalised who are at risk because of the privacy invasions of data-intensive systems. Across the globe, we see the dangers of identity systems; the harms of online violence against women and the…
Content type: Report
In December 2018, the National Coalition of Human Rights Defenders-Kenya published a report analysing the needs and concerns of human rights defenders (HRD) in relation to privacy, data protection and communications surveillance.
A summary of their findings is below. Access the full report on their website.
Content type: Long Read
A major new report published today by Privacy International has identified alarming weaknesses in the oversight arrangements that are supposed to govern the sharing of intelligence between state intelligence agencies.
'Secret Global Surveillance Networks: Intelligence Sharing Between Governments and the Need for Safeguards' is based on an international collaborative investigation carried out by 40 NGOs in 42 countries.
Previously undisclosed documents obtained by PI via litigation in the…
Content type: Report
‘Secret Global Surveillance Networks’ is a major PI report, based on an unprecedented international collaborative investigation carried out by 40 NGOs in 42 countries.
Our research shows that, globally, the sharing of intelligence is alarmingly under-regulated, opening the door to human rights abuses. Intelligence sharing has evolved dramatically with the rise of new surveillance technologies, enabling governments to collect, store, and share vast troves of personal information, including data…
Content type: Long Read
To celebrate the hard work of privacy advocates around the world, we highlight 17 #PrivacyWins from 2017!
Content type: Long Read
To celebrate International Data Privacy Day (28 January), PI and its International Network have shared a full week of stories and research, exploring how countries are addressing data governance in light of innovations in technology and policy, and implications for the security and privacy of individuals.
Content type: Long Read
To celebrate Data Privacy Week, we spent the week discussing privacy and issues related to control, data protection, surveillance, and identity. Join the conversation on Twitter using #dataprivacyweek.
Do you live in a “smart city”? Chances are, you probably do (or at least your city claims to be). But do you know what exactly makes your city “smart”, beyond the marketing term? And what does this have to do with privacy?
Companies and governments will tell you that the more cameras, sensors…
Content type: Long Read
Privacy International is celebrating Data Privacy Week, where we’ll be talking about privacy and issues related to control, data protection, surveillance and identity. Join the conversation on Twitter using #dataprivacyweek.
Exercising the right to privacy extends to the ability of accessing and controlling our data and information, the way it is being handled, by whom, and for what purpose. This right is particularly important when it comes to control of how States perform these activities.…
Content type: Report
This report sheds light on the current state of affairs in data retention regulation across the EU post the Tele-2/Watson judgment. Privacy International has consulted with digital rights NGOs and industry from across the European Union to survey 21 national jurisdictions (Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom).…
Content type: Long Read
European Court of Human Rights Intervention
On 15 September 2017, Privacy International filed an intervention to the European Court of Human Rights in Association Confraternelle de la Presse Judiciare and 11 Other Applications v. France. This case challenges various surveillance powers authorised under the French Intelligence Act of 24 July 2015 as incompatible with Articles 8 and 10 of the European Convention on Human Rights, which respectively protect the right to privacy…
Content type: Long Read
In January 2017, Kenya’s information and communication technology regulator, the Communications Authority of Kenya, announced that it was spending over 2 billion shillings (around 14 million USD) on new initiatives to monitor Kenyans’ communications and regulate their communications devices. The press lit up with claims of spying, and members of Kenya’s ICT community vowed to reject the initiatives as violating Kenyans’ constitutional rights, including the right to privacy (Article 31…
Content type: Report
This investigation focuses on the techniques, tools and culture of Kenyan police and intelligence agencies’ communications surveillance practices. It focuses primarily on the use of surveillance for counterterrorism operations. It contrasts the fiction and reality of how communications content and data is intercepted and how communications data is fed into the cycle of arrests, torture and disappearances.
Communications surveillance is being carried out by Kenyan state actors, essentially…
Content type: Report
This stakeholder report is a submission by Privacy International (PI). PI is a human rights organisation that works to advance and promote the right to privacy and ght surveillance around the world. Privacy International wishes to bring concerns about the protection and promotion of the right to privacy for consideration in Pakistan’s upcoming review at the 28th session of the Working Group on the Universal Periodic Review.
Content type: Report
This investigation looks at how surveillance is being conducted in Thailand. The first part of the investigation focuses on the ties between telecommunication companies and the state, and the second part of the investigation focuses on attacks conducted in order to attempt to circumvent encryption.
Content type: Long Read
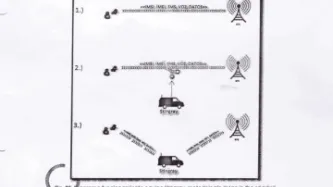
The use of IMSI catchers[1] to arrest individuals is rarely documented — as IMSI catchers are used secretively in most countries. The arrest of Colombian drug lord Henry López Londoño in Argentina is therefore a rare opportunity to understand both how IMSI catchers are used, and also the complexity of their extraterritorial use.
In October 2012, Londoño — also known as Mi Sangre (“My Blood”) — was arrested in Argentina. His arrest was the result of cooperation between the Dirección de…
Content type: Long Read
In July 2015, representatives of a private company met in a parking lot in Pretoria, South Africa to sell phone tapping technology to an interested private buyer. What they did not know was that this buyer was a police officer. The police had been tipped off that the company was looking to offload the surveillance technology, an IMSI catcher, to anyone who would buy it. It is illegal to operate such surveillance technology as a private citizen in South Africa, and illegal to buy…